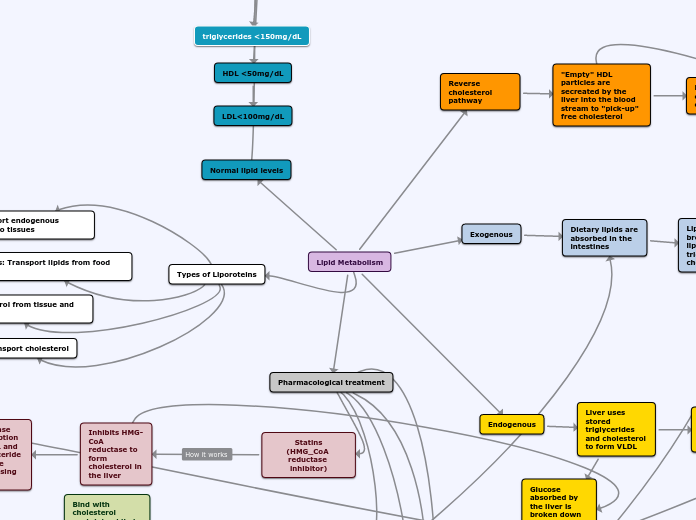
Types of Liporoteins
Fibrates
Stimulates lipoprotein lipase causing a decrease in triglycerides
Decrease in triglycerides, increases circulating HDL
Fenofibrate (Antara, Lipofen)
Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
Niacin
Inhibits synthesis of VLDL in the liver
Leads to decreased LDL and triglyceride levels
Increases HDL levels up 35%
Niacin, vitamin B12, Prescription Niacor
Cholesterol absorption inhibitor agent
Acts in the small intestines to reduce the absorption of cholesterol
Decreases circulating cholesterol that would be transferred back to the liver--decreasing hepatic cholesterol levels
Ezetimibe (Zetia)
Commonly used in conjunction with statins
Bile-acid-binding resins
Bind with cholesterol containing bile in the intestines which increases the removal of cholesterol by bodily secreation
Cholestyramine (Prevalite)
Colesevelam (Welchol)
Colestipol (Colestid)
Used in conjunction with statins
Statins
(HMG_CoA reductase inhibitor)
Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase to form cholesterol in the liver
Increase absorption of LDL and triglycerides while increasing HDL
Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Fluvastatin (Lescol XL)
Lovastatin (Altoprev)
Pravastatin (Pravachol)
Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
Simvastatin (Zocor)
Can increase blood sugar in diabetic patients
HDL particles circulate back to the liver and enter through SR-B1 or scavenger site where excess cholesterol is...
Secreted in the form of bile
Deposited into tissue
total choleterol <200mg/dL
HDL <50mg/dL
LDL<100mg/dL
triglycerides <150mg/dL
LDL: Transport cholesterol
HDL: Picks up cholesterol from tissue and transports it
VLDL: Transport endogenous triglycerides to tissues
Chylomicrons: Transport lipids from food (exogenous)
Lipid Metabolism
Pharmacological treatment
Reverse cholesterol pathway
"Empty" HDL particles are secreated by the liver into the blood stream to "pick-up" free cholesterol
HDL then combines with cholesteryl esters
HDL can also deposit cholesterol into LDL via CETP
Cholesterol is picked up by HDL from macrophages via ABCA1
Normal lipid levels
Endogenous
Liver uses stored triglycerides and cholesterol to form VLDL
Synthesis of triglycerides and cholesterol form VLDL
VLDL enters bloodstream
VLDL turns into IDL by lipoprotein lipase
Free fatty acids liberated from VLDL are stored or used as energy
IDL is converted to LDL
LDL contain a cholesterol core and triglycerides
Cholesterol is dropped off at tissues to help with cellular function such as hormone formation and form the cell membrane
LDL then travels back to the liver to be reabsorbed and can be either...
Excreted in the form of bile
Recycled and turned back into lipoproteins
Remnants of broken down VLDL are cleared by circulation or combined with LDL
Glucose absorbed by the liver is broken down with the use of HMG-C0A reductase to form cholesterol
Exogenous
Dietary lipids are
absorbed in the intestines
Lipids are broken down by lipase into triglycerides and cholesterol
Triglycerides and cholesterol bind using apoprotein "C" to form chylomicrons
Chylomicrons enter lymphatic system and travel to peripheral tissue
Apolipoprotein B-48 regulates secretion into lymph
Once chylomicrons are in peripheral tissue, lipoprotein lipase can breakdown further...
Left over "pieces" known as remnants of chylomicrons show apoprotein "E" and are brought back to the liver
Triglycerides can be stored in adipose tissue
Free fatty acids can be used as energy