da Tejas Patel mancano 2 anni
116
Memory (Human)
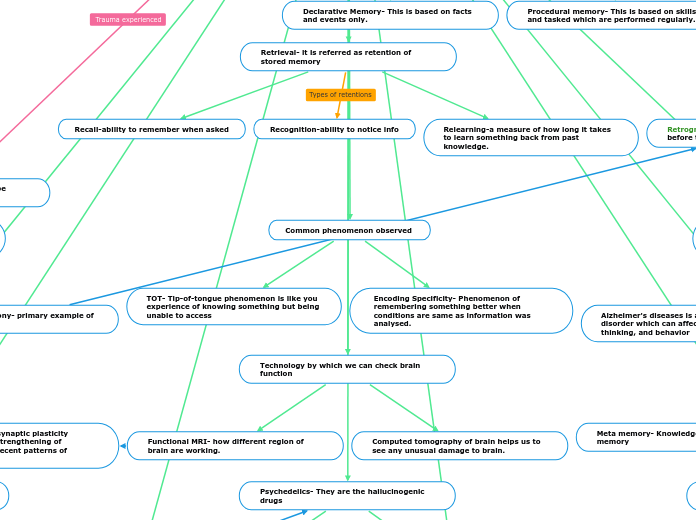
The text provides an overview of various aspects of human memory and related conditions. It highlights how memory can deteriorate with age or due to diseases like Alzheimer's and Multiple Sclerosis.
da Tejas Patel mancano 2 anni
116

Più simili a questo