NEGATIVAS
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
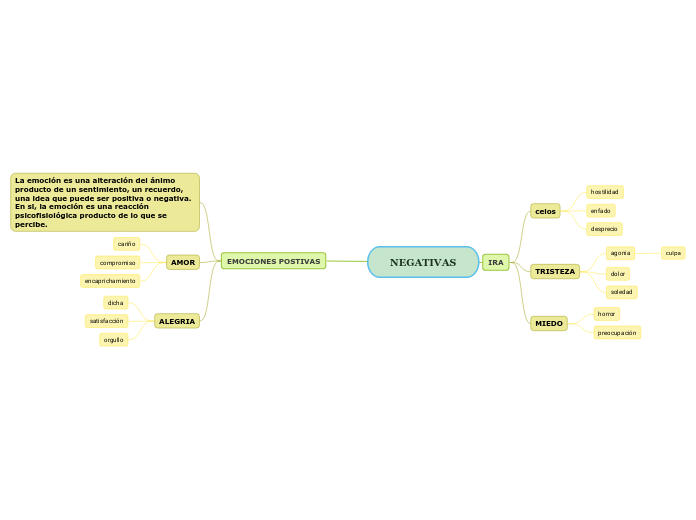
EMOCIONES POSTIVAS
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
ALEGRIA
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
orgullo
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have + Past Participle?
e.g. Will you have met your colleague by this time tomorrow?
satisfacción
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have + Past Participle
e.g. I won’t have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
dicha
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
AMOR
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
encaprichamiento
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
compromiso
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
cariño
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
La emoción es una alteración del ánimo producto de un sentimiento, un recuerdo, una idea que puede ser positiva o negativa. En si, la emoción es una reacción psicofisiológica producto de lo que se percibe.
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
IRA
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
MIEDO
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
preocupación
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
horror
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
TRISTEZA
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
soledad
Structure:
BE + Subject + Verb-ING?
Are you eating now?
dolor
Structure:
Subject + BE not + Verb-ING
e.g. You are not eating now.
agonia
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
culpa
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I am beingYou are beingHe/She/It is beingWe are beingYou are beingThey are being
Form of verb 'to have':
I am havingYou are havingHe/She/It is havingWe are havingYou are havingThey are having
celos
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
desprecio
Structure:
Do + Subject (I, You, We, They)+ V1 (First Form of Verb)?
Does + Subject (He, She, It)+V1 (First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Where does he work?
enfado
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
hostilidad
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.