da Minh Le mancano 7 anni
321
Occupational Shifts, Poverty and Productivity in Mekong Delta
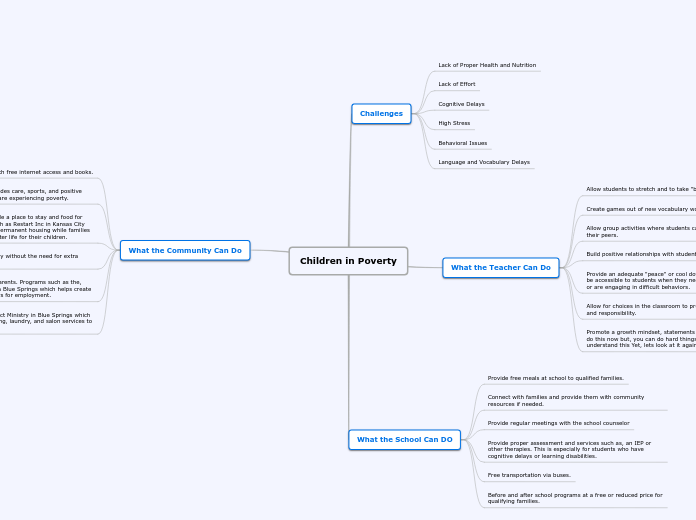
The text explores various dimensions of poverty, particularly focusing on the Mekong Delta region. It discusses key theories and models that help understand economic behaviors and issues faced by the poor, such as the Deaton Paradox and the concept of selling labor at low wages.