da JONATHAN SAJAN manca 1 anno
141
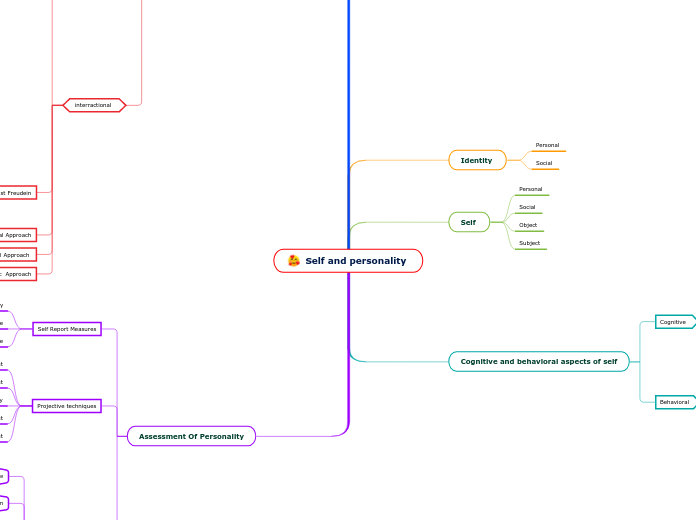
Self and personality
The study of self and personality encompasses various approaches and theories that aim to understand human behavior and identity. Classic approaches include the psychodynamic perspective, which explores stages of personality development and levels of consciousness, and the humanistic approach that focuses on individual growth and potential.