Heart
Made Up Of Tissues
Connective Tissue
Nerve Tissue
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Makes the heart contract and moves the blood around the body
Blood
Type Of Protein
Plasma
A protein-rich liquid that carries the blood cells along and makes up over half of blood’s volume.
Types Of Blood Cells
Platelets Cells
Tiny cells that help in blood clotting
White Blood Cells
These are infection-fighting cells in the blood which recognize and destroy invading bacteria and viruses
Red Blood Cells
Contains a protein called hemoglobin, which
allows them to transport oxygen throughout the body
Blood Vessels
Types
Capillaries
Tiny blood vessels with very thin walls which allow substances to diffuse between the blood and other body fluids and tissues
Veins
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart
Then travels to the small vessels
Blood exchanges many substance with the surrounding tissues
Blood flows into the veins
Blood returns back into the heart, process repeats
Trachea is supported by many rings of cartilage. The cartilage keeps the trachea open to allow air to flow freely. It is a special type of connective tissue with specialized cells mixed in a mix of strong and flexible fibers
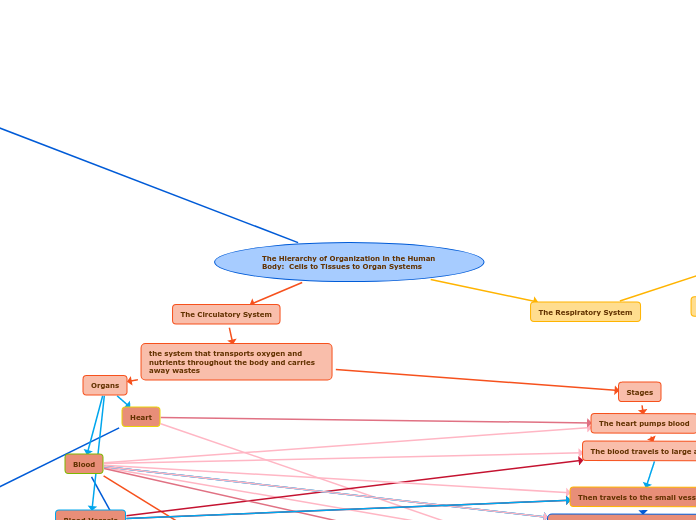
The Hierarchy of Organization in the Human Body: Cells to Tissues to Organ Systems
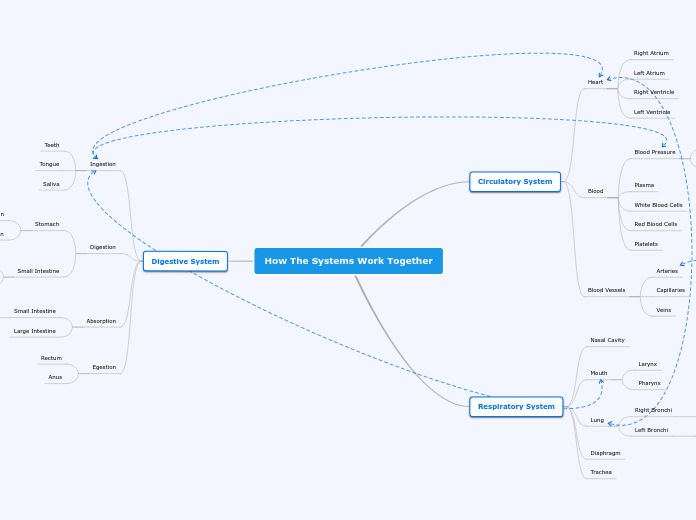
The Respiratory System
Organ system provides oxygen for the body and allows carbon dioxide to leave the body
Bronchi
Nose/Nasal Cavity
Trachea
Lungs
Air first begins to enter our body from our Moth and nose
Passes through the pharynx
Travels down the trachea
Trachea Support
Trachea divides into 2 bronchus' known as the bronchi
The Circulatory System
the system that transports oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and carries away wastes
The heart pumps blood
The blood travels to large arteries
The Digestive System
Organ system which both chemically and mechanically break down food to release nutrients molecules for our body to absorb and use
Organs
Stages
When you eat, you swallow and your tongue pushes the food into your throat.
Digestion
Breaks food down into useful nutrients
Once you begin swallowing, the food begins to move down your esophagus
Food enters your stomach, the stomach muscles mix the food and liquid then slowly empties its liquids, called chyme
Absorption
Nutrients move into the bloodstream
The food then eneters the small intestine. The muscles of the small intestine mix food with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and intestine, and push the mixture forward.
Moving into the large intestine, the large intestine absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool
To food moves down to the rectum, stores stool until it pushes stool out of your anus
Elimination
Leftover waste is removed from the body
Anus
Rectum
Appenxdix
Large Intestine
Small Intestine
Pancreas
Stomach
Liver
Esophagus
Salvary Glands
Mouth
Pharynx