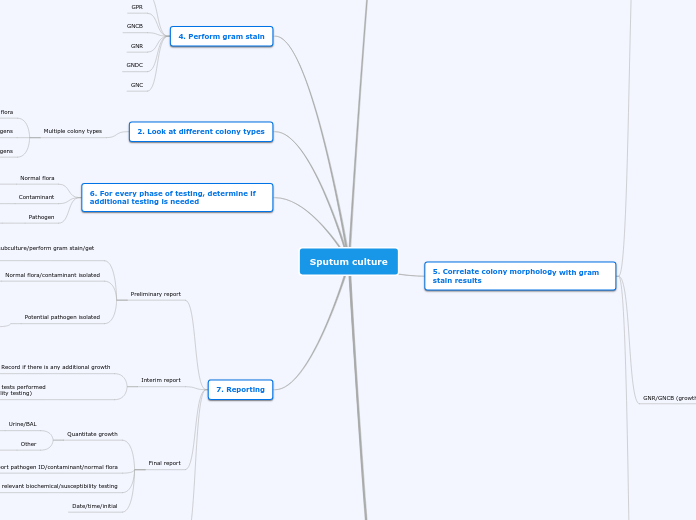
Sputum culture
7. Reporting
ALWAYS date/time/initial reports, beginning of overnight tests, susceptibility testing, etc.
Final report
Date/time/initial
Note relevant biochemical/susceptibility testing
Report pathogen ID/contaminant/normal flora
Quantitate growth
Other
Quantitate qualitatively (i.e. many, few, etc.)
Urine/BAL
Quantitate numerically (i.e. >100,000 CFU/ml)
Interim report
Run & record any more tests performed (biochemical/susceptibility testing)
Record if there is any additional growth
Preliminary report
Potential pathogen isolated
Report relevant info (i.e. LF GNR) or use abbreviated ID & quantitate
Pathogen ID known or antibiotic susceptibilities known = report as is & do not perform susceptibility testing (i.e. beta hemolytic strep is known to be susceptible to penicillin)
Pathogen ID unknown or pathogen antibiotic susceptibilities unknown = report as antibiotic susceptibility/ID pending
Normal flora/contaminant isolated
Report as normal flora/possible contaminant & quantitate
Unable to isolate colonies/subculture/perform gram stain/get colonies to grow
Report as culture ID pending
6. For every phase of testing, determine if additional testing is needed
Pathogen
Continue testing
Contaminant
Discontinue testing
2. Look at different colony types
Multiple colony types
Mixture of normal flora & pathogens
Pathogens
Normal flora
4. Perform gram stain
GNC
GNDC
GNR
GNCB
GPR
7. Use abbreviated ID if possible
1. First & foremost = always consider source type
May change battery of tests performed
5. Correlate colony morphology with gram stain results
GNR/GNCB (growth with only fastidious organisms)
Perform gram stain
GNCB with school of fish/railroad tracks
Consider other organisms
Suspect Haem ducreyi
Perform XV tests on horse BAP
X & XV growth
Haem ducreyi
Consider other organisms/repeat testing
Perform XV tests on horse BAP
V & XV growth
Haem parainfluenzae
Haem parahaemolyticus
X growth
Haem species
XV growth
Haem influenzae
Haem haemolyticus
GNR/GNCB (growth on BAP, CHOC, & MAC)
Growth on MAC
Growth on BAP
Perform oxidase
NLF
Observe swarming on BAP
Probable Acinetobacter species (if ADH/ODC -, plump GNCB, colorless/pink colonies on MAC)
Streno maltophilia (if ADH/ODC -, strong maltose oxidizer, pale yellow/lavendar colonies on BAP)
Perform spot indole
Ampicillin R
ODC -
Prot penneri
ODC +
Ampicillin S
Prot mirabilis
Prot vulgaris
(Non-sterile body source, LF) observe lactose fermentation
(GI site) perform GNR ID panel
(Non-GI site) perform spot indole
Perform GNR ID panel
Esch coli
(Sterile body source, LF) perform GNR ID panel
G
Glucose asaccharolytic
Glucose oxidizer
ADH
LDC
Probable Elizabeth meningoseptica (if ODC -, indole +, yellow pigment)
Perform polymyxim B susceptibility
Burk cepacia complex (if ODC variable, pale yellow colonies)
Additional test results needed for definitive ID
Growth @ 42 C
Additional results needed for definitive ID
Pseudo aeruginosa (if green/red/brown pigment, LDC -, ODC - , nitrate +)
Glucose fermenter
Correlate with key biochemical reactions
GPC
Perform catalase
Possible streptococci
Gamma
Non-hemolytic strep
Alpha
Perform optochin
Strep viridans
Strep pneumoniae
Beta
Perform PYR
Perform hippurate hydrolysis
Perform bile esculin
Beta strep, not A, B, or D, or Enterococcus species
Perform 6.5% NaCl
Group D strep
Enterococcus species
Group B strep
Perform bacitracin
Group A strep
+
Perform coagulase
-
Perform bacitracin or modified oxidase
Baccitracin R/modified oxidase -
(Urine) novobiocin
R
Probable staph saprophyticus
S
Coag neg staph
(Other) coag neg staph
Bacitracin S/modified oxidase +
Micrococcus species
Staph aureus
3. Examine colony morphology
Wide variety of colony morphologies
GNR/GNCB
Gray/tan/bluish-gray/white, small, translucent, raised, convex, smooth, hockey puck
Think possible GNDC
Gray, smooth, pinpoint, flat/raised, alpha, translucent
Think possible GPC in chains
White/gray, smooth, raised, beta or gamma, opaque
Think possible GPC in clusters or chains