da felipe chavarria mancano 5 anni
290
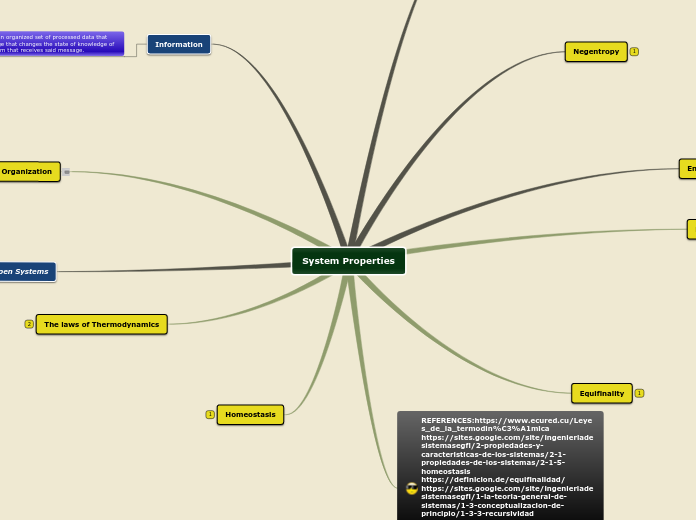
System Properties
Systems possess properties such as recursivity, where components within a larger system also exhibit system-like characteristics, making them independent yet interconnected. Organizations, as administrative structures, aim to achieve goals through the collective effort of people, leveraging human talent and social interactions.