da lormag01 :v mancano 2 anni
161
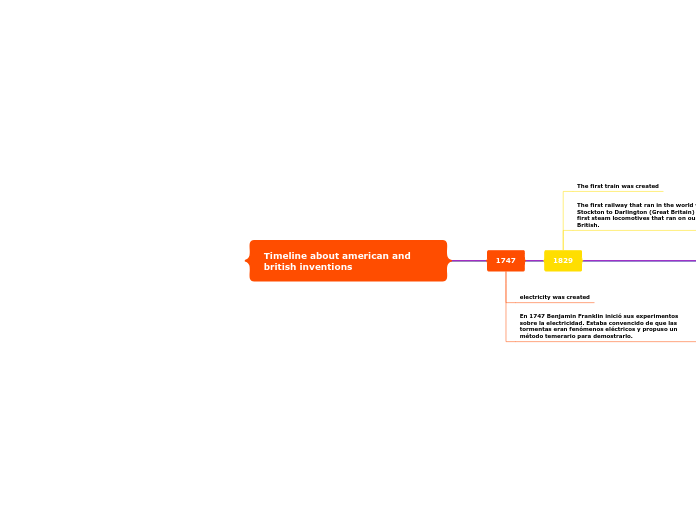
Timeline about american and british inventions
Throughout history, both American and British inventors have made significant contributions to technological advancements. In 1747, Benjamin Franklin began his experiments with electricity, laying the groundwork for future innovations.