da Julian Sandoval mancano 6 anni
260
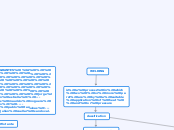
WELDING PROCESS
Welding encompasses various methods where materials are joined through the application of heat and/or pressure. Fusion welding involves heating materials until they liquefy and merge.
da Julian Sandoval mancano 6 anni
260

Più simili a questo
friction welding
(solid state welding process) coalescense is produced by utilizing the heat obtained from the mechanically induced rotating motion between the rubbing surface.
ultrasonic welding
diffusion welding
laser beam welding
is defined as a fusion welding process and coalescence is achieved by utilizing the heat obtained from a concentrated coherent light beam and impinging upon the surface to be joined.
electron beam welding
is definet as a fusion welding process wherein coalescence is produced by the heat obtained from a concentrated beam of high velocitye electron.
oxyfuel welding
this process is also known as oxi-acetylene welding heat is supplied by the combustion of acetylene in a stream of oxygen.
resistance welding
is a group of welding process in which coalescence is produced bay the heat obtained from the resistance of the work to the flow of electric current in a circuit of which the work is a part and by the application of pressure.
welding arc
this is an arc welding process wherein coalescence is produced by heating the workpiece with an electric arc setup between a flux-coated electrode and the workpiece
plasma arc welding(PAW)
This process is similar to TIG. A non-consumable electrode is used in this process. arc plasma is a temporary state of gas.
gas-tungsten arc welding(GTAW)
this process is also known as tungten-inert gas (TIG)welding. this is similar to the gas metal Arc welding process.
gas-metal arc welding(GMAW)
Is an process gas inert as argon, helium,carbon dioxide or a mixture of them are used to prevent atmospheric contamination of the weld
flux-cored arc welding(FCAW)
is similar to the shielded-arc stick welding process with the main difference being the flux is inside the welding rod.
submerged arc welding (SAW)
This is another type of arc welding process, in which coalescence is produced by heating the workpiece with an electric arc setup between the bare ectrode and the work piece.
shielded-metal arc (SMAW)
this is process wherein coalescence is produced by heating the workpiece with an electric arc setup between a flux-coated electrode and the workpiece