The signals only move in one direction:
Brain
Learning Process
Emotional effect on memory
Brain areas
Lower Brain (Reactive Brain)
It reacts to information instinctively
Prefrontal cortex (Thinking Brain)
It will consciously process and reflect the information (through thinking)
Sensory information
Positive
Thinking and learning are enhanced.
The information will enter the cortex.
Negative
Thinking and learning are inhibited.
The information will not enter the cortex.
Memory process
Mind map
Graphic organizer
Brain and Nervous System
Type of nervous system
The Somatic Nervous System
Actively control like moving our legs and arms
The Autonomic Nervous System
Works automatically
Type of nerves
Sensory nerve
The signals are come from our skin (touch), nose (smell), eyes (sight), tongue (taste), nose (smell), and ears (hear).
Carry signals about the outside world to the brain
Motor nerves
Allow the brain to control our muscles by sending a signals to the motor nerves
Characteristics
Utilizes 20% of body’s energy
consume 20% of total body oxygen
Consist of about 100 billion neurons
Consist of approximately 75% water, 10% fat and 8% protein
Represent 2% of body weight
1.5 kg or 3 pounds
Brain Theory
Herman Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI)
Quadrant D : Holistic
Synthesising
Intergrating
Intuitive
Holistic
Quadrant C : Sensitive
Emotional
Kinesthetic
Feeling based
Interpersonal
Quadrant B : Organized
Detailed
Planned
Sequential
Organized
Quadrant A : Logic
Quantitative
Fact-based
Logical
Analytical
The Triune Brain Theory
Reptilian complex
Reliable but tend to be rigid and compulsive
Controls the body’s vital functions
Influence the behavior
Unconsciousness
Value the judgment made
Responsible for emotions
Neocortex
Flexible
Consciousness
Infinite learning capabilities
Abstract thought imagination
Development of human language
Brain Waves Theory
Delta wave, ẟ
Regeneration
Healing
Theta wave, θ
Alpha wave, α
Learning
Beta wave, β
Judgment
Analysis
Decision making
Problem solving
Right Brain-Left Brain Theory
Right Hemisphere
Controls the left side of the body
Left Hemisphere
Controls the right side of the body
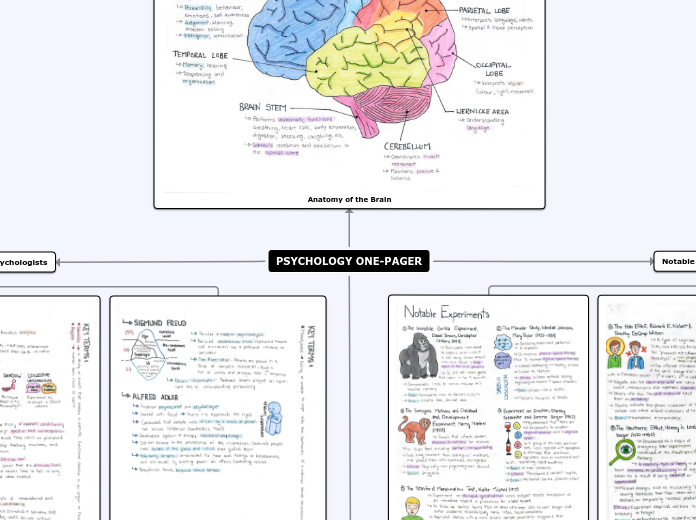
Brain structure
Function
Reptilian Brain
Cerebellum
Some memory acquisition for reflex motor acts
Muscle tone
Balance and equilibrium
Sensory representation
Control motor movement coordination
Brain Stem
Sensory alertness
Sense of balance (Vestibular function)
Controls life supporting functions of the nervous system
Limbic System
Thalamus
Relays sensory signals to and from the spinal cord and the cerebrum
Olfactory Cortex
Identification of odors
Hypothalamus
Sleep-wake cycle regulation
Food and water intake regulation
Maintain autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system
Maintains homeostasis
Hippocampus
Send and retrieves memory from long-term storage in the cerebral hemisphere
Indexes
Amygdala
Memory
Hormonal secretions
Cerebral Cortex
Parietal lobes
Intellect
Sensory information processing
Occipital lobes
Visual information
Temporal lobes
Language and speech production
Emotional responses
Auditory perception
Frontal lobes
Memory acquisition
Reasoning
Forward and critical thinking
Movement