Death investigation process
Forensic pathology
expert of testimony
Summoned to court under a subpoena
event has legal or civil proceedings
Diseases
disease has a heritable component
Examine all organ systems of the body
interpret contributed to or caused death
Injuries
- Blunt force
- Sharp force
- Firearm
- Asphyxia
- Environment
collection of trace evidence
evidence that link decedent with another individual
evidence that may indicate sexual activity
Forensic entomology
Succession pattern of insects
Non scientific identification
Circumstantial evidenc
documents
belonginigs
Distinctive marks
Physical attributes/profiling
congenital conditions
healed injuries
stature
sex
age
Visual identification
factors of death
microbiology
non-vaccinated
immunocompromised
Infection
toxicology
Intoxication with drugs
poisoning
Medicolegal autopsy
steps
Clinicopathologic diagnosis
Provide opinion on cause of death
Summarize findings in report
Ancillary studies
Internal examination
Look for disease/injury
Dissect organs and tissues
External examination
Trauma
Collect biologic samples
Collect physical evidence
History, Scene & Circumstances
Medical and social history
clothing
body position
Environment
Scientific identification
Medical hardware
Medical device with unique serial number
Radiology
Comparison of distinctive markings or characteristics
Deoxyribonucleic acid
mitochondrial DNA comparison
Nuclear DNA
Odontology
distinctive configuration of bony structures of jaw
teeth roots and nearby sinuses
Comparison of dental fillings
Fingerprint comparison
based on finger ridge patterns
Medicolegal Systems
Coroner certifies manner of death
In Canada and USA, Coroner may be physician
medical examiner
Certifies cause and manner of death
Performs death investigation
Qualified pathologist; training in death
investigation/forensic pathology
Objectives of death investigation
6. Recognize practices / conditions that could have led to death
5. Manner of death: “by what means”
4. Cause of death: “how”
3. Location of death: “where”
2. Time (date) of death: “when”
1. Identification of decedent: “who”
Roles
Provide expert testimony
Document disease processes
Document injuries / Interpret
postmortem time interval and time of injury
Degree of decomposition
identification of an unknown decedent
Determine cause, mechanism, and manner of death
determines cause of death by performing autopsy
investigation of cause and manner of death by the performance of medicolegal autopsies
through genetic testing
through recommendations
information to agencies that provide benefits
plan for health policies
data for population statistics on morbidity/mortality
provide answers to living family members
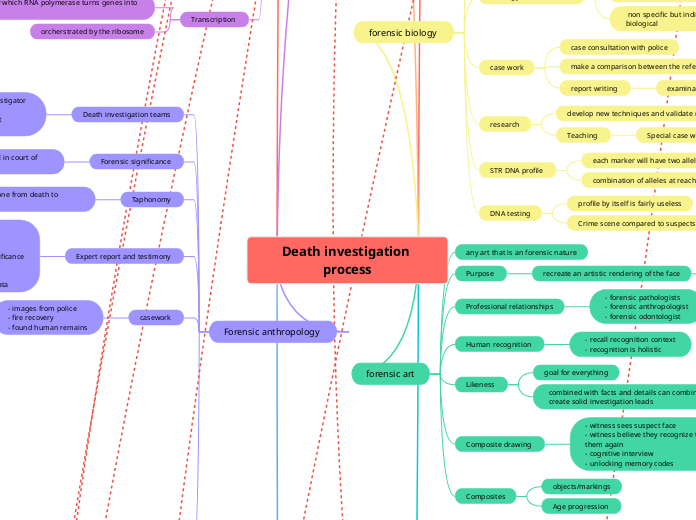
Forensic anthropology
expertise
field to lab to court
- reconnaissance
- search design
- search
- recovery
- documentation
- analysis
- expert witness testimony
- aid the forensic pathologist
- identification
Analysis
Biological profile
- age
- sex biogeographical affiliation
- stature
- trauma/pathological conditions
mini- minimum number of individuals
Chain of custody
Document any item removed from scene
Recovery and transportation
- method matches specimen
- bones
Documentation
- occurs at each step
- mapping
Search methods
- line searching
- walking
- hands and knees
- uphill/downhill
- equipment
Search design
- direct or remote
- terrain
- time of year
- hazards
- search purpose
- budget
- available personnel
Reconnaissance
- Do not enter the scene
- aerial photograph
- maps contemporary
- perimeter photography, video, sketches ]
- intangible evidence
casework
- images from police
- fire recovery
- found human remains
Expert report and testimony
- reports submitted
- relevant case info
- all parties attending
- statement of forensic significance
- biological profile
- analytical findings
- expert interoperation of data
Taphonomy
effects of environment on bone from death to recovery
Forensic significance
material to criminal investigation/trial in court of law
- Re-evaluated throughout analysis
- basis of full search
- always significant until proven otherwise
Death investigation teams
- police homicide investigator
- forensic pathologist
- forensic odontologist
- ballasts
genetics
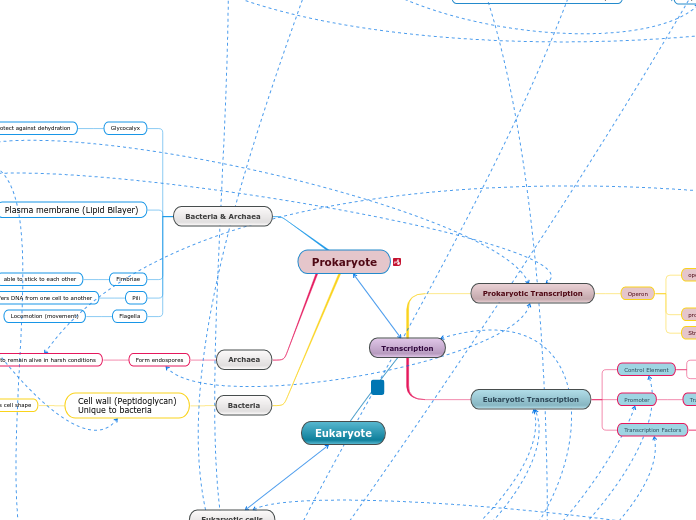
Transcription
orcherstrated by the ribosome
process by which RNA polymerase turns genes into RNA
DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid
enzyme that synthesizes new DNA from existing DNA template
Two stranded that coil around each other to form a double helix
Galton says traits
Phenotypes grade imperceptibly from one category to the next
Mendel's law
Third law
States that recessive alleles will always be masked by dominant alleles
Second law
law of independent assortment
states that alleles segregate equally and independently
Polygenic traits
interaction of several genes
Incomplete dominance
one allele not completely dominant over other allele
Co-dominance
phenotypes produced by both alleles clearly expressed
Multiple alleles
only two allele pedigrees, whereas in nature, genes can exist in several different forms
whereas in nature, genes can exist in several different forms
Non mendelian genetics
don’t explain some patterns of genetic inheritance
one-gene equals one-phenotype
some muscular dystrophies
cystic fibrosis
Sickle cell anemia
Mendelian traits are controlled by a single locus
mendelian genetics
invisible factors ; predictably determining trait of an organism
inheritance
living things have set of characteristics/traits
inherited from parents
Injury interperation
Types of injuries
firearm
types
shotgun
machine gun
handgun
single- shot pistol
derringer
revolver
Wound pattern depends on
exit gunshot wound
external beveling
slit-like appearance
stellate
irregular
entrance gunshot wound
bones
internal beveling
circular or “punched out”
range of fire
Pathologic range of fire
Distant / Indeterminate
Intermediate
Close
Contact
distance between the firearm muzzle and tissue
type of ammunition used
type of firearm used
environment
extremities
epidural or extradural heat
white translucency of corneas
Soft tissues burn away and bones can fracture
fire
External Examination
skin
burn marks
Protrusion of abdominal contents
Longitudinal splits
Due to heat effect
Body with pugilistic attitude
Smoke inhalation
Burns and thermal injuries
Hot environment
Heat stroke
Environmental hyperthermia
heat exhaustion
Cold environment
Hypothermia
Frostbite
electricity
Lightning strike
Electrocution
Asphyxia
Chemical asphyxia
Displacement of oxygen
Cyanide
Hydrogen sulfide
Carbon monoxide
pressure
Autoerotic asphyxia
Choke holds
Hanging
Ligature strangulation
Manual strangulation
Mechanical asphyxia
Crush asphyxia
Positional asphyxia
body position compromises breathing
Traumatic asphyxia
large heavy object compressing chest
Pressure on the outside of the body
classifying
Drowning
Plastic bag asphyxia
Chemical asphyxia
External next compression
Mechanical asphyxia
Death due to cerebral asphyxia
Failure of cells to receive or use oxygen
defense wounds
injury is blunt or sharp
alive and alert at the time of injury
caused by pointed/sharp edged
Chop wound
heavy sharp object creating the wound
Incised wound
straight edges
deep wound
Stab wound
sharp edges around wound
depth of wound
during active defense from weapon
Blunt force
calculation
Force = mass x acceleration = kilogram x (meter / second2)
Force varies with mass of object
nversely varies with the duration
Abrasion
removal of superficial layer of skin
produced from
destruction of superficial layers by compression
friction against a rough surface
patterned abrasion
imprinted/stamped onto the skin
Imprint of the object
Variation of an impact abrasion
impact abrasion
Scrape/brush abrasion
Contusion
Bruise
Fracture
break in the bone
Laceration
tear in tissue
caused by
shearing
crushing force
occur when
blunt object / surface
produces
crushing
tearing
shearing
scraping
strikes with
struck with
Manner of death
undetermined
yielded
insufficient evidence for any
specific classification
responsible
joint investigation
rail deaths
transportation safety board
rail investigators
fire death
emergency management
fire marshal
Homicides
police
Post scene analysis
deaths investigated
specified natural
coroner jurisdiction
collect/analyze forensic evidence
Investigation power
compel law
any finding legal
delegate power
non warranty authority
extract info
seize anything
enter/inspect
warranty authority
burial
post mortem
body possession
speaking to families
warrant for post mortem
scenes to treat carefully
answer five questions
what they need
Who
DNA
prints
documents
demographics
how
medications
circumstances
medical history
by what means
where
evidence body
demographics
what
purpose
in public interest
stages
reporting
verification
post scene analysis
scene analysis
preparation
notification
public health
police services
pathologist
consultant
other agencies
forensic scientist
Canadian death investigation
coroner
forensic art
Composites
Age progression
objects/markings
Composite drawing
- witness sees suspect face
- witness believe they recognize them of they saw them again
- cognitive interview
- unlocking memory codes
Likeness
combined with facts and details can combine to create solid investigation leads
goal for everything
Human recognition
- recall recognition context
- recognition is holistic
Professional relationships
- forensic pathologists
- forensic anthropologist
- forensic odontologist
recreate an artistic rendering of the face
of an unidentified individual
any art that is an forensic nature
forensic biology
DNA testing
Crime scene compared to suspects
profile by itself is fairly useless
STR DNA profile
combination of alleles at reach
each marker will have two alleles
Teaching
Special case work
Audits
Cold cases
develop new techniques and validate new tech
case work
report writing
examinational testing and interpretations
make a comparison between the reference samples
case consultation with police
Serology evidence exam
non specific but indicated potential presence of biological
testing performed to look biological fluids
evidence submitted from investigators/police
justice system
scientific analyses
CSI
forensic laboratory
law enforcement
laws police training
police agencies
Human genome project
Genes are approx 5% of human DNA
Mapped entire human genome
Entomology
study of insects and other arthropods
Board Certified Forensic Entomologist
practice of medico-legal entomology
research
promote education
beetles
beetles eat larvae
blowflies
life cycle
egg
pupae
larvae
adult
Applications of forensic entomology
- Post mortem interval
- Neglect
- Endotoxicology
- Extracting human DNA
- Disposal of body
- Movement of the body after death
disposal of body
Feed on tissue around a wound, destroying evidence
Larvae may move clothing to appear like a sexual assault took place
location will affect decomposition and insect colonization
larvae tissue
extracting human DNA
post mortem interval
Insects are cold blooded
develop faster at warmer temperatures
entire period after death
stages of decomposition
Chemical breakdown occurs
few morphological changes are observed
bloated
obvious odor present at this time
bloated appearance
active decay
due to the gases escaping from the body
very strong putrid odor
dry stage
insects are still present at this stage.
arcass has been reduced to bones
advanced decay
large amount of the flesh removed
odor is less obtrusive than in the previous stage
Death investigation
Autopsy
manner
circumstances surrounding death
suicide
accidental
undetermined
homicide
natural,
mechanism
asphyxia
final physiological derangement
cause of death
strangling
physiological derangement in the body
medicolegal
forensic
obscure/unnatural
sudden/suspicious
does in legal authority
clinical
hospital
extent of disease to treat descendant
treating with consent
reportable deaths
death in care
during work
prison
psychiatric hospital
long term care facility
non natural
accident
overdose
disease/sickness not treated by qualified medical expert
suddenly/unexpectedly
during/following pregnancy
medical misadventure
malpractice
misconduct
negligence
violence
objectives
public health and policy
post- mortem interval
manner of death
cause of death
identification
Purpose
assist in administration of justice
population statistics on morbidity/mortality
prevent similar deaths
provide answers to family members
Experts
medical examiner
Medical doctor
chief/deputy chief
forensic pathologist
police homicide investigator
coroner
roles
determining cause/circumstances for
unnatural deaths
unexpected deaths
unexplained deaths
access decedent medical records
determine need for further tests/investigators
order investigations or inquests
physician or “lay” person
forensic pathologist
Roles
collection of trace evidence
provide expert testimony
document injuries/interpretation
document disease process
determine cause/manner of death
identifiy unknown descendent
forensic odontologist
forensic biologist
forensic entomologist
forensic toxicologist
forensic anthropologist
Evidence
anatomical
the body
in
ingested items
projectiles
fluids
near
weapons
on
fluids
Subtopic
trace
fingerprints
abrasions
changes
abnormal
wounds
chemical damage
punctures
trauma
normal
pathological
age related change