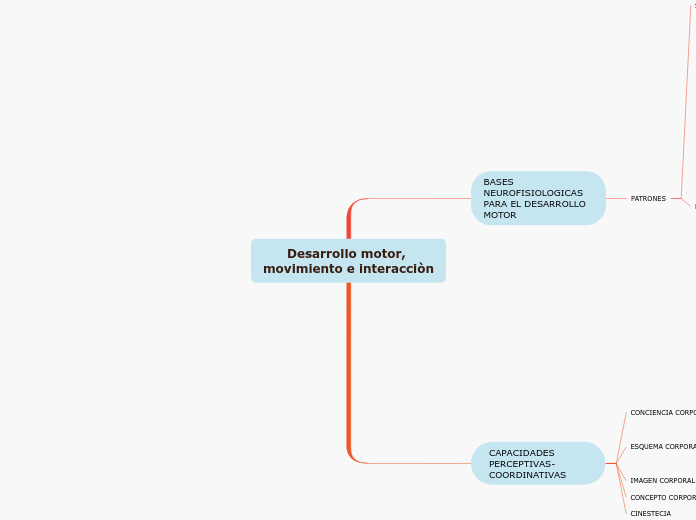
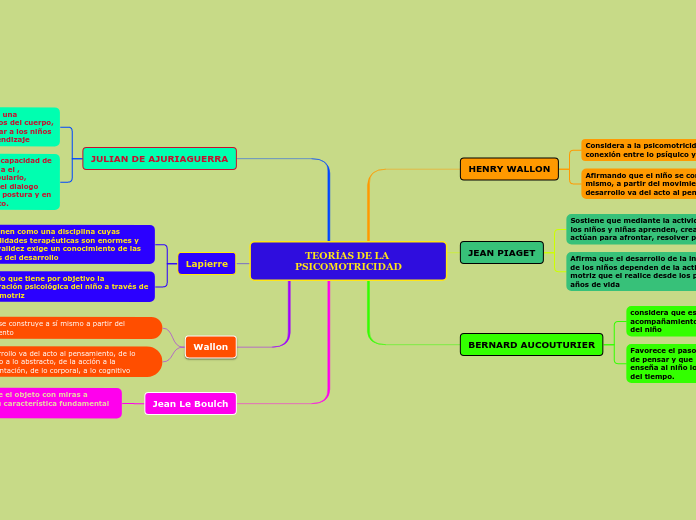
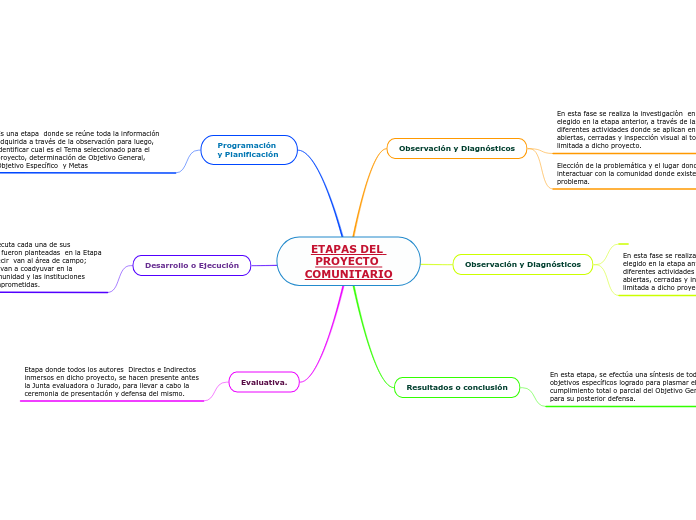
Desarrollo motor, movimiento e interacciòn
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
CAPACIDADES PERCEPTIVAS-COORDINATIVAS
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
CINESTECIA
CONCEPTO CORPORAL
IMAGEN CORPORAL
ESQUEMA CORPORAL
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
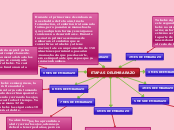
ETAPAS DE ESTRUCTURACION
Try answering these questions to come up with a closure:
- Have all the problems been solved?
- Is there a clear picture of what happens with each character in the story?
- Has the challenge transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
DE LOS 6,7 A LOS 11 AÑOS
DE LOS 2 A LOS 4 AÑOS
DEL NACIMIENTO A LOS 2 AÑOS
CONCIENCIA CORPORAL
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
BASES NEUROFISIOLOGICAS PARA EL DESARROLLO MOTOR
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
PATRONES
PERCEPCION
VISUAL
LA MEMORIA VISUAL
PATOLOGIAS
ASOCIATIVAS
APERCEPTIVAS
SEGUIMIENTO VISUAL
CUATRO TIPOS DE MOVIMIENTOS
DE SEGUIMIENTO
DE CONVERGENCIA
COMPENSATORIOS A LOS MOVIMIENTOS
RAPIDOS Y CORTOS
PERCEPCIÓN VISUAL
TACTIL
ESPINO-TALAMICA
SENSACIONES SEXUALES
SENSACIONES DE PRURITO
SENSACIONES DE TACTO NO DISCRIMINATIVAS
SENSACIONES TERMICAS
DOLOR
CORDONES POSTERIORES
SENSACIONES DE PRESIÓN
SENSACIONES SINESTESICAS
SENSACIONES EN LA PIEL
SENSACIONES FISICAS
SENSACIONES TACTILES
AUDITIVO
MEMORIA AUDITIVA
SEGUIMIENTO AUDITIVO
ONDA SONORA
ALTURA
TIMBRE
INTESNSIDAD
SENSORIALES