Engineering Physics Option
B.1 Rigid bodies and
rotational dynamics
Torque
Torque from couples (opposite direction, same magniute) cause twice the felt torque, meaning it can be multiplied by two.
Clockwise torque opposes counterclockwise rotation
Clockwise can be considered positive
Counterclockwise can be considered negative
T=Frsin(theta)
r is distance from force applied to the centre of rotation (point)
This can be considered any point, meaning torque will be at equilibrium when considering at any point
Torque is zero if it goes through the axis of rotation
Rotational force, the component that is perpendicular from the line of action through the point
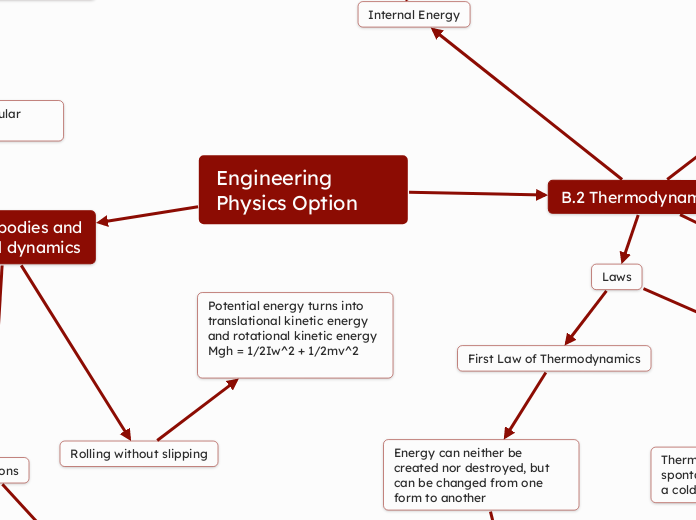
Rolling without slipping
Potential energy turns into translational kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy
Mgh = 1/2Iw^2 + 1/2mv^2
Equations
Conservation of angular momentum
Angular momentum is conserved unless acted upon by an external torque.
The area under a torque-time graph is equal to the change in angular momentum
Rotational and translational equilibrium
Translational equilibrium when resultant force is 0
Rotational equilibrium when the resultant torque on an object is 0
Moment of inertia
Ability to resist changes to its rotational motion
Sum of the mass of all the particles in an object multiplied by their distance to the axis squared
Rotational analog of mass
B.2 Thermodynamics
Internal Energy
Internal energy is the sum of the random kinetic energy of the molecules and their total potential energy. Since there are no IMFs in a gas under the kinetic molecular theory, there is no potential energy. Internal energy is equal to total KE of molecules summed.
Thermodynamic Cycles
A sequence of processes which change the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas, but eventually returns it to its initial state
The work done by a thermodynamic cycle is equal to the area enclosed by the shape formed by the cycle on a pV graph
Carnot Cycles
Isothermal expansion, Adaiabtic expansion, Isothermal compression, adiabatic compression
No heat engine operating between two reservoirs can be more efficient than a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs
The efficiency of a cycle is equal to the ratio between the useful work done and the energy put into the cycle
ncarnot = 1 - Tcold/Thot
Entropy
Entropy increases when heat is added and decreases when heat is removed
Change in entropy is defined as the change in heat of a system divided by its temperature (when temperature is constant)
Change in S = change in Q/T
Measure of the “amount of disorder” present in a thermal system
Types of Processes
Graphical Representation (adiabatic is steeper than isothermal)
Adiabatic
No thermal energy is transferred between the gas and its surroundings (Q = 0)
Process must be rapid and the gas must be well-insulated
Isovolumetric
Volume remains constant, no work is done by or on the gas (W = 0)
Isobaric
Pressure remains constant
Isothermal
Temperature (and internal energy) remain constant (ΔU = 0)
System must be in contact with a large reservoir (something outside the system that either provides or absorbs heat) and the process must be slow
Sign Conventions
Work Done
W = F * d cos(theta)
In a gas cylinder, W = pressure*A * displacement (x)
W = P * change in V
Laws
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Kelvin
A consequence of this is that the entire universe will eventually be filled with degraded (useless) heat
In a cyclic system, it is impossible to completely convert heat to work
Clausius
Thermal energy cannot be spontaneously transferred from a cold body to a hot body
Planck
Any process which appears to locally decrease the entropy of a system (a fridge makes air cool) is always accompanied by an increase in entropy elsewhere (the fridge’s coolant pump gets hot)
In an irreversible process, the total entropy of an isolated system increases, and in a reversible process, the total entropy of an isolated system remains unchanged
Thermal energy always flows spontaneously from a hot to a cold body
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can be changed from one form to another
If a quantity of energy Q is supplied to a gas, it can either gain internal energy or do work
Q=change in U+W