Meiosis
Meiosis l
Metaphase l
Chromosomes line up by pairs
Telophase l and Cytokinesis
Two haploid cells with two sister chromatids
Anaphase l
pairs separate
Prophase l
Chromosomes pair up and exchange segments
Crossing Over
exchange of genetic material between homologous pairs
Meiosis ll
Telophase ll and Cytokinesis
four haploid cells with two sister chromatids
Anaphase ll
Prophase ll
Metaphase ll
Cell Cycle
Mitotic phase
Mitosis
Phases of Mitosis
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes decondense, and spindle fibers disassemble.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equator, spindle fibers attach to kinetochores.
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible, nuclear envelope breaks down.
Cytokinesis
Interphase
Phases of Interphase
G2 Phase
More Growth of cell and cell synthesizing of proteins for cell division
End of G2 completions
Nucleus contains one or more nucleoli
Nucleus with envelope seen
Each centrosome contains 2 centrioles
Two centrosomes formed by duplication
S Phase (DNA SYNTHESIS)
DNA Synthesis and DNA Replication occur resulting in duplication of chromosomes
G1 Phase
Growth of Cell and acquires materials for DNA synthesis
Translation
Termination
ribosomes reach top codon - UAG, UAA, or UGA
Site A accepts release factor - release factor breaks hydrolysis bond between P site tRNA and the last amino acid.
subunits break apart
Occurs in the nucleus of Eukaryotes
tRNA
A site - Aminoacyl tRNA binding site
E site - exit site
P site - peptidyl-tRNA binding site
Elongation
tRNA and amino acid
Translocation - ribosome translocates tRNA in A site to P site.
empty tRNA in P site is moved to E site to be released
mRNA with tRNAs bring the next codon to be translated into the A site.
codon recognition - anticodons bind to mRNA codons in A site.
peptide bond formed
removal of polypedtide from P site to attach to A site.
Initiation
small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA
start codon - AUG (Met)
large subunit - rRNA with protein called initiation factors.
initiator tRNA in the P site.
A site available for tRNA with the next amino acid.
occurs in the cytosol of prokaryotes
Experiments Finding DNA
Hershey and Chase
Batch 2
DNA found
Batch 1
protein found
Messelon and Stahl Experiment
Medium containing N
intermediate medium
less dense medium
Fredrick Griffith Experiment
Bacterial strands
Heat killed S strand
S strand
R strand
alive mouse
Heat killed S strand + R strand
dead mouse
DNA Replication
DNA starts on the Origin of replication
Helicase , Topoisomerase and SSB begin to unwind the DNA into two different strands, creating a replication fork
Primase creates a strip of RNA primer so DNA Polymerase III can begin synthesizing the Leading and lagging strands
Lagging Strands go opposite of the leading strand
Also reffered to as Okazaki Fragments
Once synthesized, DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primer and replaces with DNA
Ligase binds the DNA together, completing the process
Leading strands go towards the replication fork, synthesizing 3' to 5'
Proteins used in DNA replication
DNA Polymerase III
Synthesizes new DNA strand by adding nucleotide to the 3' end of a pre exisitng DNA strand or off the RNA promer
DNA Polymerase I
Removes the RNA primer from the synthesized DNA strand
SSB proteins
Binds to the Single stranded DNA after Helicase unwids the double helix, making sure the DNA can be used as a template
Ligase
Binds the 3' end of the DNA that replaced the primer to the eading strand and "glues" together the Okazaki fragments from the lagginf strand
Helicase
Unwinds parental double helix at replication forks
Primase
Sets an RNA primer so DNA polymerase III can create the leading strands and lagging strands
Topoisomerase
Goes ahead of the helicase to releive "overwinding" of the DNA to ensure replications
lacZ, lacY, lacA
beta galactosidase, permease, beta transacetylase (respectively)
permease: allow the bacterial cell to take up sugar like lactose
beta-galactosidase: hydrolyzes lactose to produce galactose and glucose; glucose is preferred by bacteria cell
transacetylase: transfers an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to beta-galactosides
RNAP
lacI gene
constitutive
negative regulation
positive regulation
operon
The operon comprises an operator (the on/off switch) followed by a cluster of functionally related genes.
lac operon
lactose present, glucose present
operator
When glucose is available in the bacterial cell, the operon will be off in which the repressor will bind to the operator. However, when the glucose is used completely, the operon turns on and the repressor will unbind and instead bind to allolactose. Beta-galactosidase, permease, and transacetylase will be translated from the mRNA to catabolize lactose, to make more glucose.
off and then on
lactose present, no glucose
adenyl cyclase
cAMP
CAP
promoter
allolactose
on
no lactose
repressor
operator
off
cluster of functionally related genes
Crystallin gene expressed due to activators binding enhancer
crystallin gene not expressed due to repressor
DNA bending protein
TATA box
RNA polymerase II
transcription factors
general
basal level transcription
enhancers
upstream or downstream of gene
activators
high level transcription
repressors
reduce high level transcription
Gene Regulation
in prokaryotes
in eukaryotes
combinatorial control of gene expression
lens cell (eye)
albumin gene not expressed due to repressor binding enhancer
Liver cell
albumin gene expressed due to activators
gene expression
DNA ligase
DNA polymerase II
nuclease
Nucleotide Excision Repair
thymine dimer
mutant type amino acids:Met Stop
mutant type mRNA: 5'- AUG UAG UUU GGU UAA-3'
wild type amino acids: wild type amino acids: Met Lys Phe Gly Stop
mutant type amino acids: Met Lys Phe Ser Stop
mutant type mRNA: 5'- AUG AAG UUU AGC UAA-3'
wild type amino acids: Met Lys Phe Gly Stop
mutant type amino acids: Met Lys Phe Gly Stop
wild type amino acids: Met Lys Phe Gly Stop
Mutations
frameshift
occurs in the event of 1 to 2 insertions or deletions of 1-2 nucleotides
sickle cell anemia
Nonsense
missense
wild type mRNA: 5' AUG AAG UUU GGC UAA
silent
mutant type mRNA: 5'- AUG AAG UUU GGU UAA- 3'
wild type mRNA: 5'-AUG AAG UUU GGC UAA- 3'
secrete enzymes such as
glycoprotein
polypeptide
vesicles
Protein transport
free ribosomes
signal sequence
SRP
signal peptidase
Once the the signal peptide is cleaved, the polypeptide is released from the bound ribosome and folds into final conformation
trans-face of golgi body
amylase, insulin, casein, albumin, and collagen
Amylase- a digestive enzyme found in lysosomes
insulin- a peptide hormone
casein- a milk protein
albumin- a serum protein
collagen- an extracellular matrix protein (gives plasma membrane increase tensile strength)
G3P
18 ATP
12 NADPH
NADP+ reductase
oxygen (O2)
ATP
NADPH
chloroplast
Photosynthesis
calvin cycle
two turns of the Calvin cycle are required to produce glucose
carbon fixation
rubisco
ribulose bisphosphate
Photorespiration
light reactions
stroma
thylakoid space
H+ ions
The hydrogen ions want to go with its chemical gradient in which ATP synthase allows for passage to the stroma, which has a low hydrogen ion concentration. ATP is produced when hydrogen ions pass through ATP synthase.
Non-cyclic flow of electrons
cyclic electron flow
thylakoid membrane
Photosystem II (P680)
photosystem I (P700)
chlorophyll
reduced
carbon dioxide
6CO2 +6H20 + Light ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Oxidized
water
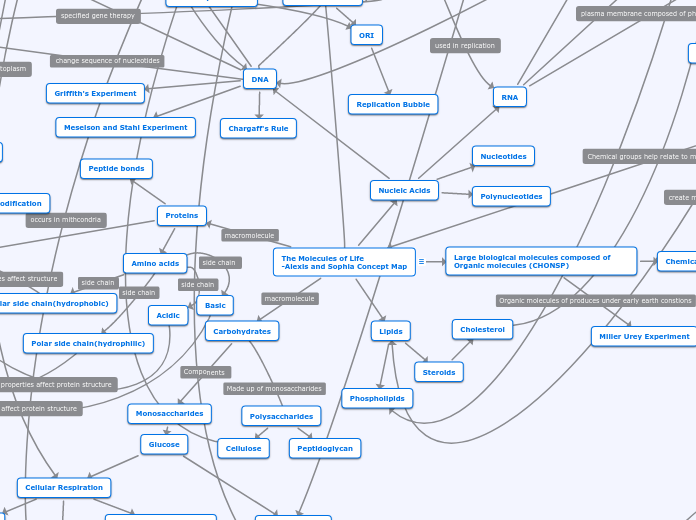
Organic Molecules
lipids
fatty acids
glycerol
nucleotides
proteins
amino acids
carbohydrates
sugars
substrate level phosphorylation
ATP synthesis
Floating topic
Acetaldehyde
formed from the breakdown of ethanol
used for synthesis
NADH and FADH2 produced from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and citric acid cycle
NAD+ Regeneration
bacteria pathway
oxidizing
2 ATP made in citric acid cycle
anaerobic conditions
aerobic conditions
Fermentation.
Lactic Acid
lactate
produced from exercise and metabolism
breaks down sugars
makes ATP
Alcohol
converts sugars to ethanol and carbon dioxide
3 Step Process
3.) ETC and Chemiosmosis
ATP Synthase
occurs in the inner membrane
protein complexes
Matrix of mitochondrion
Citric Acid Cycle
produces 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 after both acetyl CoA molecules enter and complete the cycle
1.)Glycolysis
pyruvate oxidation
Electron carrier NAD+ is reduced from the electrons from Pyruvate to produce NADH. A carbon is released from Pyruvate and produces carbon dioxide and a CoA molecule is joined with the remaining two carbons of Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA enters the citric acid cycle
Energy pay off phase
2 NADH produced
Energy investment phase
Glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
Phospholipid Bilayer
Attatchment site
Selectively permeable
Fluidity
Hydrophobic Tail
Hydrophilic Head
Cell Membrane
Membrane Receptors
In target cells that receives the signal molecule.
ion channel receptor
Ligand gated ion channel receptor acts as a gate for ions to pass and change shape.
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
when phosphate groups are added to tyrosines
Autophosphorylation
When each polypeptide on dimerization functions as a kinase so it takes phosphate groups from ATP and adds it to the other polypeptides.
protein kinases
enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to proteins
2 polypeptides
the polypeptides dimerize when a signal molecule is bound to them.
can add phosphate groups to something
Dimer
when a signal molecule binds it activating monomers to allow them to come together forming a dimer.
Interacting proteins
the activated tyrosine kinase receptor can now interact with other proteins for responses from the cells.
3 stages
3rd reception
2nd reception
1st reception
Membrane receptor
present on the plasma membrane
second messenger
needs help of the other molecules inside cells
They are small, nonprotein, water soluble molecules/ions that are used in signal transduction to relay a signal within a cell.
Synthesized from ATP using enzyme Adenylyl Cyclase
carbon monoxide
nitric oxide
Ca^2+
cGMP
cyclic AMP
Adenylyl Cyclase
converts the ATP to cAMP
Gene expression
mRNA are converted into proteins
can turn off some genes
Protein synthesis
Changes the activity of metabolic enzyme and open/close of ion channels
First messenger
Signal molecule is hydrophilic
G protein coupled receptor
Guanosine diphosphate, GDP, inactive form.
Guanosine triphosphate, GTP, active form
Binds GPCR
The single molecule binds to GPCR during reception
converting to GTP
G protein binds to the GPCR converting the GDP to GTP on the G protein
Activation of G protein
Happens when GTP binding
activate enzyme
the G protein can activate the enzyme
Intercellular receptors
present in the cytoplasm, in the nucleus
1. passes through the membrane
The signal molecule can bind if nonpolar or hydrophobic so it can pass the lipid bilayer and bind a receptor once inside the cell.
2. activation
The hormone binds to the receptor protein and activates it.
3. binds to specific genes
The hormone enters the nucleus and binds to specific genes.
4. protein acts as transcription factor
stimulating the transcription of the gene into mRNA
5. mRNA translated into protein
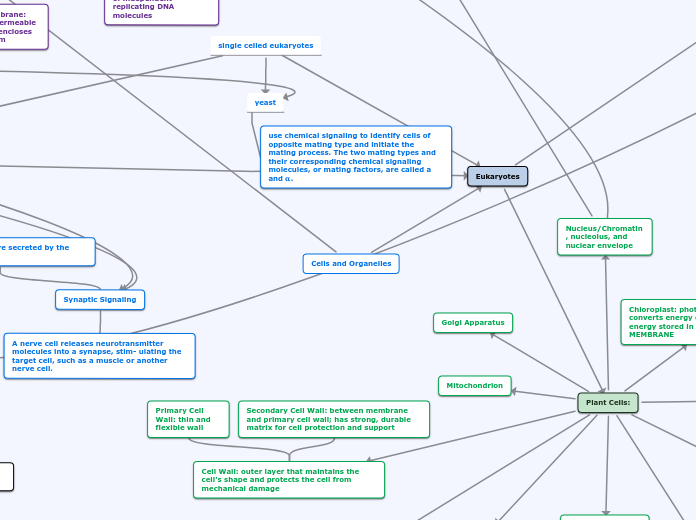
Cell Signaling
Nuclear envelope
Outer membrane
inner membrane
Nuclear pores
Functions of Membrane Protiens
Intercellular Joining
Signal Transduction
Binding to ECM
Enzymatic Activity
Cell-Cell Recognition
Transport
cell structures and functions
Eukaryotes
Cell Types
Plant
Cell Wall
Plasmodesmata
Animal
ECM
Cell junctions
Tight
Gap Junction
Desmosomes
Mitochondria
Named the powerhouse of a eukaryotic cell, as it generates ATP
Cell components
Cytoskeleton
Microfilaments
Actin
myosin
Intermidate Filaments
Microtubules
Tubulin
Nucleus
Chromatin
Nucleolus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Central
Contractile
Food
ADP
ATP
Hydrogen pump
Golgi apparatus
Vesicles
Endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Er
Smooth ER
Fats
Saturated
Unsaturated
Phospholipids
Steroids
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are split into Domain Archaea and Domain Bacterial
Domain Archaea
Extreme halophiles
Archaea that lives in highly saline environments
Extreme thermophiles
Archaea that thrives in very hot environments
Methanogens
Methanogens are Prokaryotic domain archaea cells that live in swamps and marshes to produce methane as a waste product.
metabolism
obligate aerobes
requires o2 for cell respiration
Facultative anaerobes
uses O2 when present, uses fermentation when O2 is not present.
obligate anaerobes
use of fermentation anaerobic respiration
Fimbriae
helps with attachment
DNA location
Ribosomes
protein synthesis takes place
Plasma membrane
membrane that enclosing the cytoplasm
cell wall
structure outside the plasma membrane
Glycocalyx
outer coating consists of a capsule of a slime layer
Flagella
movement structure
Heterotroph
Heterotrophs get carbon from organic compounds
Photoheterotroph
Chemoheterotroph
Chemotrophs get their energy from organic chemicals.
Autotroph
Autotrophs use inorganic carbon sources
Photoautotroph
phototrophs obtain energy from the light
Chemoautotroph
Chemotrophs get their energy from inorganic chemicals.
Domain Bacterial
Endospore
Endospores serve a purpose for survival under harsh environmental conditions.
Capsules/ slime layers
helps resists against phagocytosis and adherence to surfaces
peptidoglycan
cell wall filled with peptidoglycan. Helps bacteria with support, protects the cell, and maintains the shape.
pili
bacteria mating
Periplasmic Space
Periplasmic space contains hydrolytic enzymes and binding proteins for nutrient processing/ uptake.
Gas vacuole
Buoyancy of floating in aquatic environements
Plamid
DNA that is separate from the main bacterial chromosome
Nucleoid
DNA location
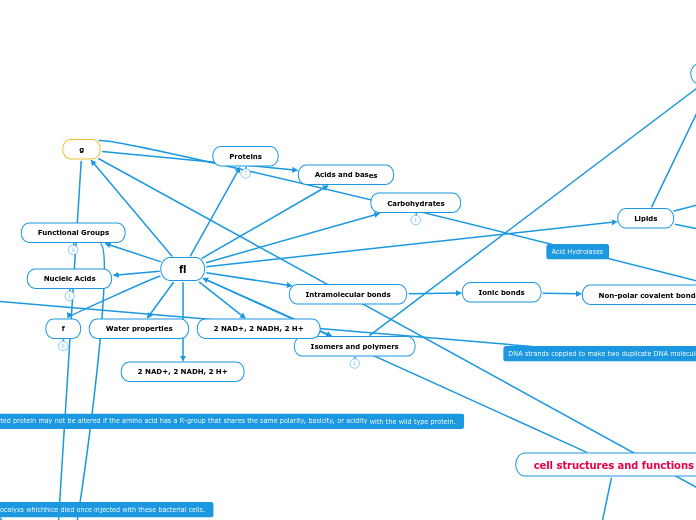
Intramolecular bonds
Ionic bonds
Non-polar covalent bonds
Polar covalent bonds
Connected through amino and carboxyl groups between mainchains
Transport Protiens
Carrier Proteins
Channel Proteins
Subtopic
Membrane Proteins
fl
2 NAD+, 2 NADH, 2 H+
Nucleic Acids
Phosphodiester bonds
Proteins
Protein Structures
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quartenary
Amino Acids
Peptide bonds
Carbohydrates
Simple sugars (Monosaccharides)
Lipids
Functional Groups
Methyl (CH3)
Amino (NH3+)
Carboxyl (COO-)
Carbonyl (CO-)
Sulfhydrl
Hydroxyl (OH-)
Isomers and polymers
Enantiomers (Chirality)
g
Acids and bases
Water properties
f
Intermolecular interactions
Hydrogen bond
Ion dipole
Dipole-dipole
Hydrophiobic interactions
London dispersion