IMMUNOLOGY
Work
The immune system is tightly regulated
regulatory or suppressor T cells, inhibitory cytokines
clonal anergy(เซลลืฝ่อไปเองสามารถตอบสนองต่อantigen)
Elimination of self-reactive cells
Memory
จดจำantigenและสามารถตอบสนองทันทีเมื่อantigenเข้ามารอบที่2และมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
Clonal selection
T-cell and B-cell ที่ถูกเลือกต้องมีปริมาณมากพอต่อาการตอบสนองantigenแต่ละชนิด
Adaptive Immunity
T cell receptors (TCR)
B cell receptors (BCR)
Innate Immunity
Receptor
Mannose receptor
Scavenger receptor
Toll Like receptor
integrated system of host defense
การทำงานร่วมกันระหว่างInnate and adaptive immunity
distinguish between self and non-self
ระบบภูมิคุ้มกันต้องแยกได้Self(ไม่ต้องตอบสนอง) and non-self(ตอบสนองกับสิ่งแปลกแปลม)
Type
Adaptive /acquired/specific immunity
Humoral Immune Response(ตอบสอนงพึ่งสารน้ำ)
Secondary Immune Response
Primary Immune Response
Cell-mediated Immune Response(การตอบสนองพึงเซลล์)
Inate /non specific immunity
Component
Humoral Substances(สารน้ำ/โปรตีนที่อยู่ในเลือดหรือสารคัดหลั่ง)
Acute phase protein(สร้างขึ้นเมื่อมีการติดเชื้อหรือการอักเสบ)
Cytokines
Complement
Immune Cells
Lymphoid
NK-cell
B-cell
T-cell
Myeloid
Monocyte/macrophages/dendritic cell(phagocytic cell)
Granulocytes
Organs &Tissues
Cutaneous associated lymphoid tissue
Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue
Lympnode
Thymus
Liver
Function
Surveillance(กำจัดเซลล์ที่ทำงานผิดปกติ)
กำจัด cancer cell
Hemeostasis(กำจัดเซลล์ที่หมดอายุ)
ทำลายRBCหมดอายุ
defense(ป้องกันสิ่งแปลกปลอม)
Epitope or Antigenic Determinant
มี 2 group
Epitope ที่ถูกจดจำด้วยB-cell/antibody
B cell epitope
Conformation determinant
Linear determinant
Protein, Polysaccharides, nucleic acid, etc.
Epitope ที่ถูกจับด้วยการจดจำโดยTCR
T cell epitope
Protein/Peptide about 8-15 residues
มี 3 form
Neoantigenic determinant
Linear determinat
Conformational determinant
ส่วนย่อยของantigenที่จดจำโดยantibody, B-cell receptor, T-cell receptor
Adjuvant
thetic polynucleotide
Liposome
Monophosphoryl lipid A
uminium hydroxide
Freund’s adjuvant
Incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (IFA)
without the mycobacterial components
Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)
composed of inactivated and dried mycobacteria,
เพิ่มการตอบสนองantigenชนิดใดชนิดหนึ่งแบบไม่จำเพาะ
สารเคมีที่สามารถปรับเปลี่ยนการตอบสนองร่างกายต่อสารอื่น
Mitogen
สารเคมีที่สามารถกระตุ้นทำให้เกิดการแตกตัวหรือเพิ่มจำนวนได้
Others substance
Dextran, polyvinylpyrolidone, trypsin
Product of Microoganism
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) : T and B cells
Lipopolysacharide (LPS) : B cells
Phytomitogen : plants
Pokeweed mitogen (PWM): T and B cells
Concanavalin A (Con A) : T cells
Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) : T cells
Hapten
made immunogenic by conjugation to a suitable carrier
reacts with specific antibody but is not immunogenic
Immunogen
Specific reactivity (Antigenicity)
สามารถจับantibody and T-cellอย่างจำเพาะ
Immunogenicity
Immunogen สามารถกระตุ้นการทำงานเซลล์ภูมิกันได้
สารที่กระตุ้นให้สร้างhumoral or cell-mediated immune response
Antibody
TCR
recognize peptides
Macromolecules
nucleic acid and proteins
phospholipids
Complex carbohydrates
Simple intermediate metabolites
Sugar
lipid
autacoids
hormone
สามารถจับกับสิ่งแปลกปลอมหรือสารอื่นๆได้หลายชนิด
Subtopic
Antigen
คุณสมบัติ
Other factors
Structure and Accessibility of epitopes
Chemical Complexity
มีโปรตีนเป็นองค์ประกอบจะดีที่สุด
Molecular Weight (MW) (> 6,000 Da
Foreignness
ชนิดของAntigen
T-dependent antigen
Epitope ไม่ซ้ำกัน
Cells
Virus
Hapten-carrier complex
Glycoprotein
Protein
เป็นantigenกระตุ้นT-cell hrlpให้สร้างB-cell
T-independent antigen
ลักษณะEpitope เหมือนกัน ซ้ำๆกัน
Cell surface of microbe
Ficoll
Dextran
จำเพาะB-cell
แบ่งสองกลุ่ม
Autoantigen
(พบในร่างกาย)
Own cell and molecule
Heteroantigen(สิ่งแปลกปลอม)
Microbial antigen
Bacteria, virus
Non-microbial antigen
bstance from plant, animal, human
สารที่สามารถจับได้จำเพาะกับ antibody และT-cell
สารที่เหนี่ยนำทำให้สร้างantibodyได้
History
Edward Jenner
สะกิดฝีด่างหนองจากวัวมาใส่คน
เกิดการผลิดVaccinia(L. vacca = cow)
smallpoxlesion (การสะกิดแผลฝีด่างมาบดเป็นผงแล้วสูดดม)
Variolation (การเสริมภูมิคุ้มกัน)
Meaning
รากศัพท์ immunitas or immunis
การศึกษาการต่แต้านจุลชีพหรือสิ่งแปลกปลอม
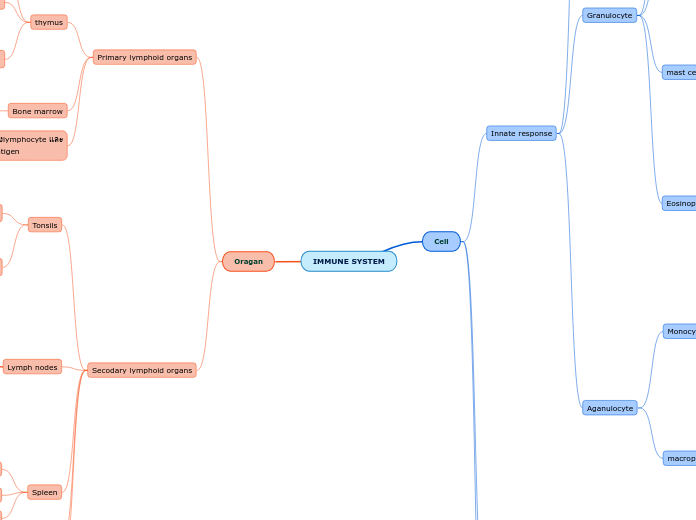
IMMUNE SYSTEM
Oragan
Secodary lymphoid organs
Appendix
Peyer's Patches
Spleen
Red pulp
ทำลายRBCที่หมดอายุ
Marginal zone
เป็นตัวแบ่งแยกระหว่างwhite pulp and red pulp
White pulp
T-lymphocyte is around the vessels called periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS)
Lymph nodes
องค์ประกอบสำคัญ
Medullary sinus: Macrophage
Medulla: Plasma cell
Paracortex: T cells
Cortex: B cells
เป็นตัวกรองน้ำเหลืองก่อนเข้าสู่กระแสเลือด
เป็นที่อยู่ของ T-Cell and B-cell
เป็นตัวดักจับantigen and present antigen เพื่อให้lymphocyteมาจับกิน
Tonsils
ตัวกรองและตัวจับanyigen
เป็นเยื่อเมือกที่อยู่บริเวณคอ
Lingual
Palatine
Adenoid
Tubal
Primary lymphoid organs
เป็นแหล่งสร้างหรือความจำเพาะของlymphocyte และในส่วนนี้จะไม่มีการตอบสนองต่อantigen
Bone marrow
แหล่งสร้างเม็ดเลือดทุกชนิดและเป็นแหล่งเจริญเติบโตของ B-cell
thymus
ทำหน้าที่
เป็นcellพี่เลี้ยง เพื่อหลั่งฮอร์โมนให้T-cellเกิดการพัฒนาขึ้น
เป็นที่คัดเลือก T-cell ที่สมบูรณ์
thymus gland
cortex
จะมีT-cell ตัวอ่อนระจายตัวอยู่หนาแน่น (สีเข้ม)
medulla
จะมีT-cell ตัวแก่กระจายตัวอยู่สม่ำเสมอ (สีอ่อน)
แหล่งสร้างและเพิ่มจำนวน T-cell
Cell
Antign presrnting cells
the dendritic cells
เป็นตัวนำเสนอต่อWBCอื่นๆ
เป็นสะพานเชื่อมระหว่างinnate and Adaptive response
Adaptive response
Lymphocytes
B lymphocyte
ผลิตplssmacell เพื่อสร้างantibody
NK cell (NKT cell)
ทำลายแบบไม่จำเพาะ:ทำลายเซลล์มะเร็ง
แอลฟ่าแกมม่า T lymphocytes 1-10%
T lymphocytes
ตัวควบคุมT lymphocyte
cytotoxic CD8+ ส่งสัญญาณให้ Ab in MHCI
helper CD4+ ส่งสัญญาณ Ag in context of MHCII
Innate response
Aganulocyte
macrophages
ถูกกระตั้นให้อยู่ภายในเนื้อเยื่อ
Microglial cells-Brain
Sinusoidal macrophages-Spleen
Osteoclast - BM
Mesangial macrophage - kidney
Alveolar macrophage-Lung
Kupffer cells-liver
Monocytes
Non-classical monocyte(พบน้อย)
CD14+CD16+
Classical monocyte(พบเยอะ)
CD14+CD16-
อยู๋ในกระแสเลือด
มีการกินแบบphagocytosis
Granulocyte
Eosinophils
กำจัดปรสิต โดยทำลายผนังเซลล์ของปรสิตและจะมีIgEมาเกาะเพื่อหลั่งcytokine เพื่อกระตุ้นWBCตัวอื่นมาช่วยกำจัดสิ่งแปลกปลอม
ควบคุมการหลั่งhistamine
มีการกับกินแบบphagocytosis แต่ทำงานได้ไม่ดีเท่ากับneutrophil or macrophage
ติดสีส้ม-แดง เนื่องจากภายในเป็นเบสจึงติดสีที่มีคุณสมบัติเป็นกรด
mast cells
จะมีIgEมะรองรับ
อยู่ภายเนื้อเยื่อเกี่ยวพัน
ตอบสนองต่ออาการภูมิแพ้
กระตุ้นWBCตัวอื่นให้ไปบริเวณที่เกิดการอักเวบ
หลั่งสารhistamine
Basophils
มีการจับAbs กับIgE ทำให้เกิดการหลั่งhistamineเพื่อเพิ่มการผ่านของเหลงในหลอดเลือดทำให้เกิด swelling,red,heat
ตอบสนองต่อภูมิแพ้
Non-phagocytic
พบในเนื้อเยื่อ <1%
Neutrophils
เมื่อมีการอักเสบจะเป็นตัวแรกที่เคลื่อนไปยังบริเวณอักเสบ
มีการกินantigentแบบphagocytosis
ทำลายเชื้อโรค เนื่องจากมี FC เป็นreceptorที่จับกับantigentได้พอดี
ภายในติดสีได้ทั้งกรด-เบส
มีการตอบสนองต่อสารcytokineที่มากระตุ้นได้ดี
-ทำงานไม่เฉพาะเจาะจงและตอบสนองรวดเร็ว