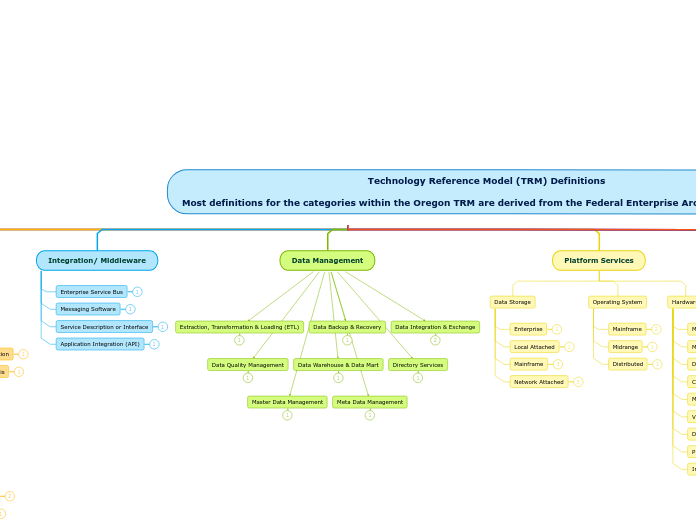
Technology Reference Model (TRM) Definitions
Most definitions for the categories within the Oregon TRM are derived from the Federal Enterprise Architecture (FEA) v2
Development & Testing Tools
Software Configuration Management
Software to track and control changes in the software including the establishment of baselines and revision control
Testing
Software that supports testing throughout the various testing levels, testing types and testing process/methodologies. Tools also collects or generate various testing artifacts including but not limited to traceability matrix, test cases and test scripts.
App Development Tools A programming tools or
Software development tools that software developers use to create, debug, maintain, or otherwise support other programs and applications.
Requirement Management
Software used to document, analyze, trace, prioritize and agree on requirements for an initiative and communicate with the relevant stakeholders.
IT Systems Management
Application Monitoring
Tools that monitor application performance and events.
System Monitoring
Tools that monitor system (server & network) performance and events.
Monitoring Tools
Software that continuously records performance, capacity use, throughput of computer hardware or Software and provides notification about deviations from normal.
Software Distribution
Software to the end user.
Software that supports the process of delivering
Mobility Management
Software that supports the administration of mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablet computers, laptops and desktop computers.
License Management
Software that supports enterprise license management. It supports the purchase, upgrade and tracking of legal usage contracts for system software and applications, written computer programs, and components.
IT Service Management
Functions support workflow and linking between incident, change, problem, and service request records with each other and with records of configuration items.
This is the set of tools that supports the maintenance and continuous improvement of the IT environment with a focus on customer needs and IT services.
Information Security
Security Controls
Encryption
Software to convert plaintext to ciphertext through the use of a cryptographic algorithm.
Digital Signature
Software to use and manage electronic signatures to support.
Virus Protection
Software used to prevent, detect, and remove self-replicating programs that run and spread by modifying other programs or files.
Authentication & Authorization
Software that supports obtaining information about parties attempting to log on to a system or application for security purposes and the validation of those users.
Cyber Security Management
Compliance
Software, processes, and procedures to ensure compliance with applicable laws, rule or order issued by an executive authority, or regulatory agency of a government and having the force of law, as intended through the supervision and oversight of operations and programs, the protection of systems and resources, and the prevention of waste, fraud and abuse.
Incident Management
Software that supports the set of capabilities to provide active response and remediation to a security incident that has allowed unauthorized access to a government information system.
Identification and Authentication
Defines the set of capabilities to support the management of permissions for logging onto a computer, application, service, or network; includes user management and role/privilege management. This includes Identification and Authentication for digital signatures.
Data Integrity & Privacy Management
Data Integrity and Privacy Management involves the coordination of data collection, storage, dissemination, and destruction as well as managing the policies, guidelines, and standards regarding data management, so that data quality is maintained and information is shared or available in accordance with the law and best practices
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous Monitoring includes all activities related to the real-time monitoring of security controls employed within or inherited by a system. (see Appendix G of NIST Special Publication 800-37)
Threat & Vulnerability Management
Threat and Vulnerability Management involves all functions pertaining to the protection of federal information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruptions, modification, or destruction, as well as the creation and implementation of security policies, procedures and controls. It includes all risk and controls tracking for IT systems.
Security Management
Major category of information security services to protect networks, computers, programs and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access. Services may include: threat and vulnerability management, continuous monitoring, data integrity and privacy management, identification & authorization, cryptography, incident response, audit trail capture & analysis, and certification & accreditation.
Network
Mobile Device Networking
Mobile Device Networking covers the sets of standards commonly used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunication services and networks that comply with specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. Such standards find applications in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV, among others.
Web & Video Conferencing
Videoconferencing is the conduct of a videoconference (also known as a video conference or video teleconference) by a set of telecommunication technologies which allow two or more locations to communicate by simultaneous two-way video and audio transmissions. It has also been called 'visual collaboration' and is a type of groupware.
Web conferencing refers to a service that allows conferencing events to be shared with remote locations. In general the service is made possible by Internet technologies, particularly on TCP/IP connections. The service allows real-time point-to-point communications as well as multicast communications from one sender to many receivers. It offers information of text-based messages, voice and video chat to be shared simultaneously, across geographically dispersed locations. Applications for web conferencing include meetings, training events, lectures, or short presentations from any computer.
Radio over IP
RoIP can be deployed over private networks as well as the public Internet.
Radio over Internet Protocol (RoIP) is similar to VoIP, but augments two-way radio communications rather than telephone calls. From the system point of view, it is essentially VoIP with PTT (Push To Talk). To the user it can be implemented like any other radio network. With RoIP, at least one node of a network is a radio (or a radio with an IP interface device) connected via IP to other nodes in the radio network. The other nodes can be two-way radios, but could also be dispatch consoles either traditional (hardware) or modern (software on a PC), POTS telephones, softphone applications running on a computer such as a Skype phone, PDA, smartphone, or some other communications device accessible over IP.
VOIP
Internet telephony refers to communications services — voice, fax, SMS, and/or voice-messaging applications — that are transported via the Internet, rather than the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The steps involved in originating a VoIP telephone call are signaling and media channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signal, encoding, packetization, and transmission as Internet Protocol (IP) packets over a packet-switched network. On the receiving side, similar steps (usually in the reverse order) such as reception of the IP packets, decoding of the packets and digital-to-analog conversion reproduce the original voice stream.
Radio Infrastructure
Radio networks are transmitted through free space by radio waves. There are two types of radio networks currently in use around the world: the one-to-many broadcast network commonly used for public information and mass media entertainment; and the two-way type used more commonly for public safety and public services such as police, fire, taxicabs, and delivery services. Many of the same components and much of the same basic technology applies to both.
Infrastructure
For the purposes of the IRM, Infrastructure, as used here, is a broad term covering the various forms of basic hardware and software that comprise the foundation of a network.
Voice Services & Infrastructure
Voice networks are sometimes dedicated, as in the original public switched telephone network (PSTN), but have changed to be a type of traffic carried on data networks using some form of packetswitching technology. Voice traffic is distinct from Data traffic in the delivery requirements (it needs to arrive nearly synchronously and be assembled in order without drop-outs) and bandwidth usage (which is high).
Data & Video Services
Video networks can be dedicated links devoted to video for large video conferencing installations. As with Voice traffic, Video is often a type of traffic carried on data networks using some form of packet-switching technology. Video traffic is distinct from Data traffic in the delivery requirements (it needs to arrive nearly synchronously and be assembled in order without drop-outs) and bandwidth usage (which is very high).
A data network type is an electronic communications process that allows for the orderly transmission and receptive of data, such as letters, spreadsheets, and other types of documents. What sets the data network apart from other forms of communication, such as an audio network, is that the data network is configured to transmit data only. This is in contrast to the audio or voice network, which is often employed for both voice communications and the transmission of data such as a facsimile transmission.
Platform Services
Hardware
Infrastructure as a Service
Cloud IaaS providers host infrastructure components for users.
A cloud computing form that provides computing resources over the Internet.
Platform as a Service
A category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage web applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app.
Desktop Services
IT support & maintenance for general enduser technologies (hardware and/or Software).
Virtualization
In computing, virtualization is the creation of a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as a hardware platform, Operating System (OS), storage device, or network resources. This section of the IRM categorizes those mechanisms to create virtual platforms.
Mobile
The purpose of an OS is to provide an environment in which a user can execute applications.
As with other operating systems, a mobile computing device Operating System (OS) is a computer program, implemented in either software or firmware, which acts as an intermediary between users of a computer and the computer hardware.
Communication Hardware
Communications Hardware refers broadly to hardware intended primarily to create a link to the network from the user or another computational device.
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system is a software system in which components located on networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages. The components interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal.
Formerly called "minicomputers”, which were hosts to dumb terminals connected over dedicated cables, most midrange computers today function as servers in a network.
Midrange computers encompass a very broad range and reside in capacity between high-end PCs and mainframes.
A Mainframe is a high-performance computer used for large-scale computing purposes that require greater availability and security. It often serves many connected terminals and is usually used by large complex organizations.
Operating System
Distributed
Operating systems that support the distributed server environment.
Midrange
A midrange computer operating system is, in simplest terms, a collection of programs that manage a computer system's internal workings - its memory, processors, devices, and file system. Midrange computers are almost universally known as servers to recognize that they often "serve" applications to end users at "client" computers, that they use a client/server computing model.
Mainframe operating systems are tailored to meet the substantially different architectures and purposes of mainframes as high-volume transaction processing devices, or the purposes of supercomputers as high-volume algorithmic processors.
A mainframe or supercomputer operating system is, in simplest terms, a collection of programs that manage a computer system's internal workings - its memory, processors, devices, and file system.
Data Storage
Network Attached
Deduplication is not a capability of this service. No security scanning is offered, resulting in additional customer requirements to use this as a storage solution. The NAS Services are used to support ETS backup services only.
The device is connected to the network, access to the device is controlled by network and firewall configurations.
Use of network attached storage (NAS) to store data, which is infrequently accessed or changed, to provide a lower cost storage solution. NAS Services offer centralized storage of data that provides faster deployment, easier maintenance, and fewer staff requirements for support.
Mainframe
Mainframe storage is available through:
2. Tape – fully redundant, Virtual Tape Storage (VTS).
1. Disk – fully redundant, fastest recovery.
Local Attached
Local Storage is considered dedicated storage: Storage on individual equipment (e.g. solid state drive, external storage array) or on a disk accessible by a single host. Local attached (non SAN) storage is exclusively for the Windows and Linux server environments. This service is mostly consumed in field / remote offices.
Enterprise
Enterprise data storage services provide highly-available, secure, and reliable disk storage for use by system operating systems, applications, application data, and for user files. This service is available to physical and virtual systems.
Data Management
Meta Data Management
Software that supports the maintenance and administration of data that describes data.
Master Data Management
Software that supports a set of processes and tools that consistently define and manage the non-transactional data entities of an organization, which may include reference data. It has the objective of providing processes for collecting, aggregating, matching, consolidating, quality-assuring and distributing such data throughout an organization to ensure consistency and control in the ongoing maintenance and application use of this information.
Directory Services
Software that supports the listing of employees and their whereabouts.
Data Warehouse & Data Mart
Database used for reporting and analysis, where the data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the transactional systems.
Data Quality Management
Software to ensure that data are fit for their intended uses in operations, decision making and planning and to ensure internal consistency of the data.
Data Integration & Exchange
Software development necessary to facilitate such integration. These elements can share function, content, and communications across heterogeneous computing environments.
Software services that enable elements of distributed business applications to interoperate and the
Data Backup & Recovery
Software that creates copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event or to restore and stabilize data sets to a consistent, desired state.
Extraction, Transformation & Loading (ETL)
Software that supports the extraction of data from a database, the manipulation and change of data to a different format and the population of another database with the data.
Integration/ Middleware
Application Integration (API)
Source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other. An application programming interface (API) may include specifications for routines, data structures, object classes, and variables (e.g., per Wikipedia).
Service Description or Interface
Software that enables various services available in SOA. It is designed to be interrogated by Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) messages and to provide access to Web Services Description Language (WSDL) documents describing the protocol bindings and message formats required to interact with the web services listed in its directory.
Messaging Software
Software that enables passing of information message between different systems and IT assets using different communications technologies.
Enterprise Service Bus
Software used for designing and implementing the interaction and communication between mutually interacting software applications in Service Oriented Architecture (SOA).
Application Components
Visualization
Photographic
Software that supports the capture, storage, and manipulation of photographic images.
Multimedia
Software to manage, develop and manipulate content from a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, still images, animation, video, or interactivity.
Idea Mapping
Software that is used to create diagrams of relationships between concepts, ideas or other pieces of information.
Graphics
Software that enables a person to manipulate static, animated or video visual images on a computer.
Data Mapping
Software that supports the process of creating data element mappings between two distinct data models. Data mapping is used as a first step for a wide variety of data integration tasks.
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Software that supports the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation and includes software or environments which provide the user with input-tools for the purpose of streamlining design processes; drafting, documentation, and manufacturing processes.
Unified Communications & Collaboration
Syndication Management (RSS Feeds)
A family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works, such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video, in a standardized format.
Event/News Management
Software that provides users with frequently updated content to which they subscribe.
Social Software
Interactive tools handle mediated interactions between a pair or group of users. They focus on establishing and maintaining a connection among users, facilitating the mechanics of conversation and talk.
Software that supports the capturing, storing and presentation of communication, usually written but may include audio and video as well.
Instant Messaging
Software that supports text, voice and/or video communications between two or more users.
Calendaring
Software that provides users with an electronic version of a calendar, an appointment book, address book, and/or contact list.
Email
Software that supports the transmission of memos and messages over a network.
E-Commerce
Licensing/Permitting
Licensing and Permitting involves activities associated with granting, revoking, and the overall management of the documented authority necessary to perform a regulated task or function.
Storefront
Solution for those who want to host a website that advertises products or services and for which consumer transactions are generated online.
Payment Processing
Includes disbursements of funds, via a variety of mechanisms, to government and private individuals, federal agencies, state, local and international governments, and the private sector, to effect payment for goods and services, or distribute entitlements, benefits, grants, subsidies, loans, or claims.
Process Automation & Management
Configuration Management
Software that controls the hardware and software environments, as well as documents of an organization.
Quality Management
Software that ensures an organization or product is consistent based on quality planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement.
Risk Management
Software that allows planners to explicitly address uncertainty by identifying and generating metrics, setting parameters, prioritizing, and developing mitigations, and tracking risk.
Project Management
Software that provides capabilities for cost estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration, communication, quality management and documentation or administration systems, which are used to deal with the complexity of large projects.
Case Management
Software or business processes of an organization.
Software that controls the process for updates or modifications to the existing documents,
Software that monitors the activities within the business cycle Change Management
Software the supports decisions, actions, business rules and other matters that govern an organization Process Tracking
Software that manages the life cycle of a particular claim or investigation within an organization to include creating, routing, tracing, assignment and closing of a case as well as collaboration among case handlers Governance & Policy Management
Business Rule Management
Software used to define, deploy, execute, monitor and maintain the variety and complexity of decision logic that is used by operational systems within an organization or enterprise. This logic, also referred to as business rules, includes policies, requirements, and conditional statements that are used to determine the tactical actions that take place in applications and systems.
Business Process Management
Software include items such as: Process Engine, Business Analytics, Content Management, and Collaboration Tools.
Software that allows organizations to abstract business process from technology infrastructure and support the managerial approach through enabling technology, bridging organizational and technology silos. Business Process Management applications and
Knowledge & Discovery Management
Knowledge Distribution & Delivery
Software that supports the transfer of knowledge to the end customer.
Knowledge Capture
Software that facilitates collection of data and information.
Modeling
Software to develop descriptions that adequately explain relevant data for the purpose of prediction, pattern detection, exploration or general organization of data.
Information Retrieval
Software that provides access to data and information for use by an organization and its stakeholders.
Data Mining
Software that provides for the efficient discovery of non-obvious, valuable patterns and relationships within a large collection of data.
Productivity
Word Processing
Software used for the composition, editing, formatting and/or possibly printing of print material.
Spreadsheet
Software used to create, update and/or read a two-dimensional matrix of rows and columns.
Presentation
Software used to display information, normally in the form of a slide show.
Drawing
Software used to create or edit a graphical object.
Geospatial Information
Imagery
Software that supports the collection of information via satellite and aerial photography.
Cartography
Software that supports the creation of maps.
Geospatial Data Analysis
Supports the application of statistical analysis and other informational techniques to geographically based data.
Geospatial Data Collection
Software that supports the collection or management of geospatial information.
Document & Content Management
Document Management System
Software used to track, store and retrieve electronic documents and/or images of paper documents. It is usually capable of keeping track of the different versions created by different users (history tracking).
Web Content Management
Software that provides content authoring, content review and approval, tagging and aggregation, content publishing and delivery, and syndication management.
Records Management
Software that supports the management and stewardship of a type of information by the federal government in order to facilitate communication and information archival.
Forms Management
Software that supports the creation, modification, and usage of physical or electronic documents used to capture information within the business cycle.
Document Library
On line repository of documents, letters, speeches, web sites, books, or articles to be shared.
Document Imaging & OCR
Software that supports the document scanning and the interpretation of images into text.
Analytics, Reporting & Statistics
Online Analytical Processing
Software that supports a process to swiftly answer multi-dimensional analytical (MDA) queries and enable users to interactively analyze multidimensional data from multiple perspectives. An OLAP consists of three basic analytical operations: consolidation, drill-down, and slicing and dicing.
Survey Data Collection
Software that supports methods to collect information from a sample of individuals in a systematic way for empirical research in social sciences, marketing and official statistics.
Portfolio Management
Software that provides the set of capabilities to support the administration of a group of investments held by an organization.
Reporting
Software tools that support the creation and display of individually designed and structured reports with self-service access to meaningful data.
Business Intelligence & Analytics
Software to support identifying, extracting, and analyzing business data, such as performance and cost metrics to support better business decision-making.
Business Process/ Systems Portfolio
Facilities Management
Software that supports facilities management including the maintenance, administration, certification, and operation of office buildings that are possessions of the State.
Physical Safety
Software that supports the management of, and mechanisms for, interaction and oversight for controlling biological, chemical, and radiological materials and wastes. This includes addressing identification of materials that need special handling and processes to minimize the risk of their unsafe use and improper disposal.
Emergency Management
Software that enables designated individuals to communicate critical information to many individuals across multiple devices.
Software that supports the continuity of operations for an organization's business through the identification of surge or temporary personnel in addition to federal staff.
Grants Management
Software that supports the administration and monitoring of grants.
Legal
E-discovery
Software that supports the analysis of electronically stored information and its exchange, including digital forensics analysis.
Human Resource Management
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as awards, benefits, education/training, employee personnel records, staff acquisition, retirement, and time & attendance.
Workforce Management
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as resource planning & allocation, skills management, and team & organizational management.
Property & Asset Management
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as facilities management, inventory management, logistics & transportation, media & facilities reservations, and warehouse management.
Financial Management
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, budget planning & execution, financial audit, general ledger, payroll and travel.
Customer Service
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as call center/help desk (supports the management of service center to respond to government and contract employees’ technical and/or administrative questions), and/or issue tracking (supports activities associated with providing an agency’s customers with information regarding the agency’s service offerings and managing the interactions and relationships with those customers).
Acquisition Management
Major category of business processes which represent functions such as invoice tracking & approval (manages inflow & outflow of “products”, as well as data about the level of “products” on hand), procurement (used in acquisition of goods or services and management of the contracts), and vendor management (used to build a list of vendors or measure satisfaction of relationships).
End-user Devices
Smart Phones
A cellular phone that performs many of the functions of a computer, typically having a touchscreen interface, Internet access, and an operating system capable of running downloaded applications.
Phones
Major category of devices and services related to telephony and telecommunications.
Laptops, PC, Tablets, Printers
Major category that represents common consumer-based technology devices.