by FRANCISCO JAVIER ZAMORA PEñUñURI 4 years ago
211
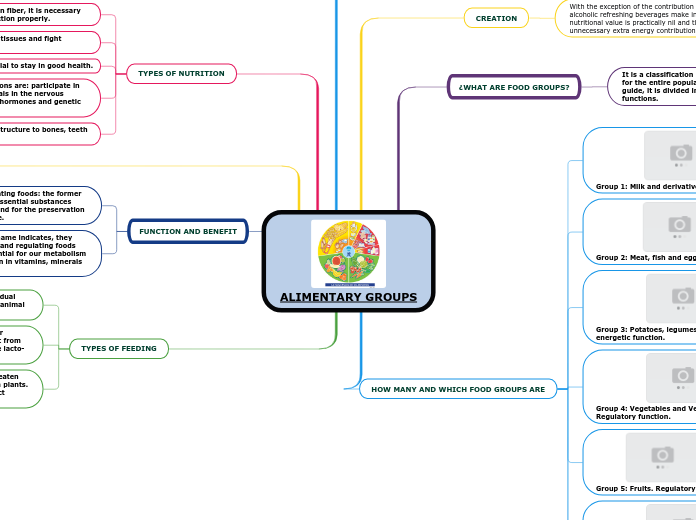
ALIMENTARY GROUPS
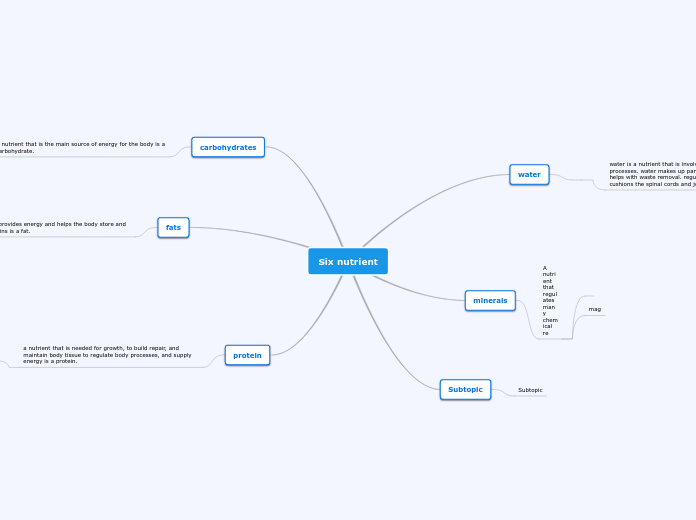
Different types of nutrients play crucial roles in our body, including carbohydrates for intestinal health, proteins for tissue repair and immune defense, minerals for bone structure, fats for overall health, and vitamins for various physiological functions.