by Leah Good 2 years ago
197
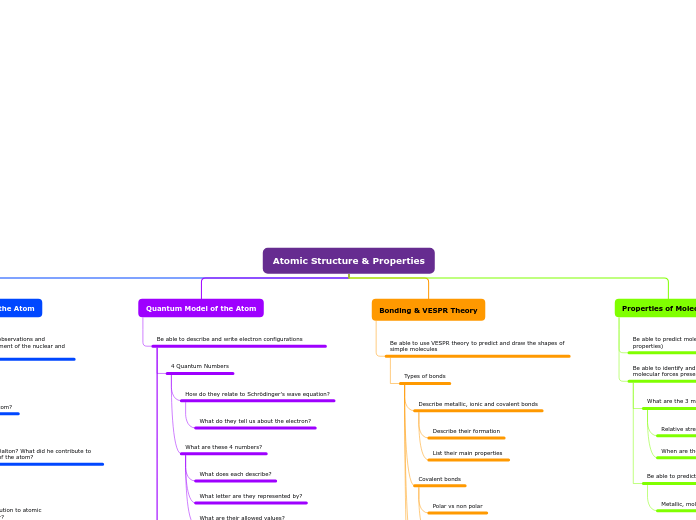
Atomic Structure & Properties
Over time, the understanding of atomic structure has evolved significantly, driven by various scientific models and experiments. Thomson's model, often referred to as the "plum pudding"
by Leah Good 2 years ago
197

More like this
Metallic, molecular, ionic, covalent networks
When are they present?
Relative strengths?
Use Lewis structures to predict VSEPR shape
Hybridization?
Bond angles?
Lewis Structures
For ionic and covalent compounds
Covalent: incomplete & expanded octet, polyatomic ions
Covalent bonds
Use EN values to predict polarity of bond
Polar vs non polar
Describe metallic, ionic and covalent bonds
List their main properties
Describe their formation
Can you easily obtain this information off of the periodic table?
What are its n, l, ml and ms values?
Again, be able to apply the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule and the Pauli exclusion principle
Define and apply the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule & the Pauli exclusion principle
Identify exceptions to the Aufbau principle
Write the shorthand/noble gas configuration as well
What are these 4 numbers?
What are their allowed values?
What letter are they represented by?
What does each describe?
How do they relate to Schrödinger's wave equation?
What do they tell us about the electron?
What does solving Schrödinger's wave equation tell us?
What is the difference between Bohr's 'orbit' & the quantum 'orbital'?
Why can't we know an electrons exact location?
What principle describes this phenomenon?
What are the key ideas of the new quantum mechanical model? (HINT: there are 2)
What are we still keeping from Bohr's model?
Where did Schrödinger & de Broglie come up with the idea that electrons behave as standing waves?
What experiment did they conduct?
Why was a new model needed?
What new discovery was made?
What couldn't Bohr's explain?
Identify the shortcomings of Bohr's theory/model
Connect the movement of electrons between energy levels to the formation of a discrete line spectrum
Apply the relationship between the energy, frequency and wavelength of light to the emission spectrum
What is a discrete vs. continuous line spectrum?
What does a discrete line spectrum tell us about the nature of the atom?
Describe what needs to happen for electrons to move between energy levels
How does light energy play a role?
What is a photon?
What do some photons have more energy than others?
What does it mean that electrons are quantized?
What are the main postulates of Bohr's atomic theory?
How did Bohr address/explain the issues associated with Rutherford's model
What did scientists identify as the 2 major issues associated with Rutherford's model?
What did the outcome of the gold foil experiment tell Rutherford about the structure of the atom?
Describe Rutherford's gold foil experiment, including what he predicted would happen, and what actually happened
Why do we still talk about Thomson? What did he contribute to our current understanding of the atom?
What is missing from his model?
What did his model of the atom look like?
What was his major contribution to atomic theory/what did he discover?
Why do we still talk about Dalton? What did he contribute to our current understanding of the atom?
What is he missing?
What is the nature of the atom?