by Tom Haug 11 years ago
714
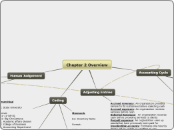
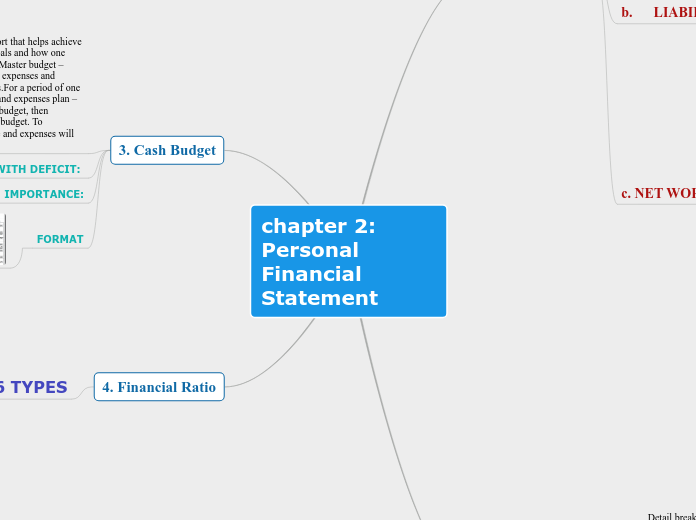
Chapter 2 Concept Map
The text delves into various aspects of accounting and coding systems, particularly within an academic context. It introduces hierarchical, block, mnemonic, and sequential coding formats, providing examples for each, such as state university identifiers and uniform systems for restaurant accounts.