by Rebecca Metko 3 years ago
210
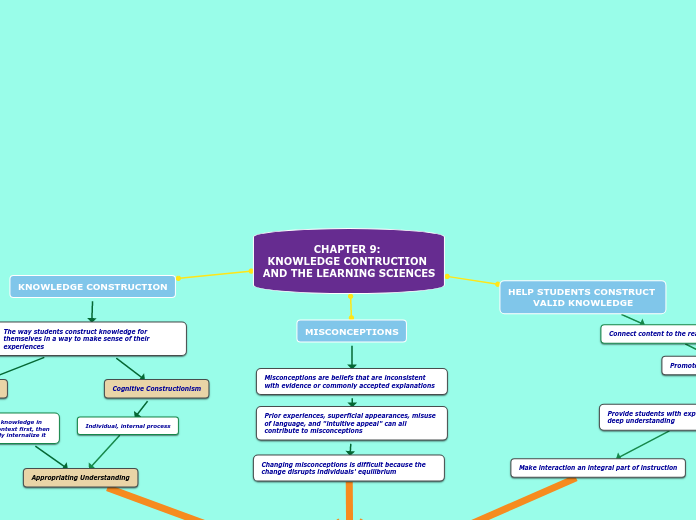
CHAPTER 9: KNOWLEDGE CONTRUCTION AND THE LEARNING SCIENCES
Misconceptions often arise from prior experiences, superficial appearances, misuse of language, and intuitive appeal, making them difficult to change as they disrupt one's mental equilibrium.