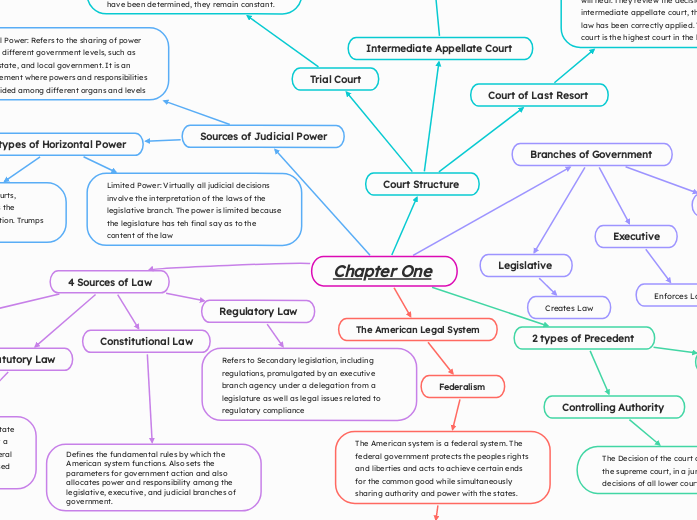
Chapter One
2 types of Precedent
Persuasive Authority
A Court is not bound to follow the precedent but does so because it is persuaded by the decision
Controlling Authority
The Decision of the court of last resort, typically the supreme court, in a jurisdiction controls the decisions of all lower courts.
Court Structure
Trial Court
First level in the court system, the level at which the fact-finding process takes place. A judge or jury hears matters of dispute, and the issues of facts are determined. When the facts have been determined, they remain constant.
Intermediate Appellate Court
Serves as an intermediate step between the trial courts and the courts of last resort in a state. In an appeal, The Appellate court reviews the decision of the trial court on the issues of law. The role of the appellate court is to ensure that the trial court did not err and to guide and develop the law within the jurisdiction. There is no Jury at the Appellate level. Appellate court is composed of 12 judges.
Court of Last Resort
The Court of Last Resort is called the supreme court in most jurisdictions. the court of Last Resort is very busy so they cannot hear every case that is appealed. The courts therefore have the power to determine which case they will hear. They review the decision of the intermediate appellate court, the mine if the law has been correctly applied. The supreme court is the highest court in the land.
Sources of Judicial Power
Vertical Power: Refers to the sharing of power among different government levels, such as union, state, and local government. It is an arrangement where powers and responsibilities are divided among different organs and levels
2 types of Horizontal Power
Supreme power: This is when the courts, especially the supreme court act as the ultimate interpreter of the Constitution. Trumps everything.
Limited Power: Virtually all judicial decisions involve the interpretation of the laws of the legislative branch. The power is limited because the legislature has teh final say as to the content of the law
Branches of Government
Judicial
Interprets Law
Executive
Enforces Law
Legislative
Creates Law
4 Sources of Law
Case Law
Refers to the published opinions of judges that arise from court cases where they often interpret statutes, regulations, and constitutional provisions.
Regulatory Law
Refers to Secondary legislation, including regulations, promulgated by an executive branch agency under a delegation from a legislature as well as legal issues related to regulatory compliance
Statutory Law
Laws passed or enacted by Congress and state legislatures. Laws written and enacted by a legislative body. For the United States federal government, statutory law is the acts passed by the United States Congress.
Constitutional Law
Defines the fundamental rules by which the American system functions. Also sets the parameters for government action and also allocates power and responsibility among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government.
The American Legal System
Federalism
The American system is a federal system. The federal government protects the peoples rights and liberties and acts to achieve certain ends for the common good while simultaneously sharing authority and power with the states.
The federal government has continued to indirectly assist states with education through categorical grants. The purpose of categorical grants has been to provide supplementary assistance to the state systems of education and to shape educational policy in the states. States then have the option to accept or reject the categorical grants.