circulatory system
Detailed breakdown
which can lead to blockages in blood vessels
Abnormal clotting of blood
leading to cell damage and potential loss of function
A disruption of blood supply to the brain
narrowing them and restricting blood flow
The buildup of plaque in the arteries
and other complications
stroke
High blood pressure that can lead to heart disease
and carbon dioxide is released into the lungs to be exhaled
oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses into the bloodstream
At the lungs' alveoli
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins
and the blood becomes oxygenated
carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen
In the lungs
Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart's right ventricle to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
and the blood becomes oxygenated before returning to the heart
oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide
At the capillaries
Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart through the veins
and eventually reaches the body's tissues
which branches into smaller arteries
Oxygenated blood is pumped from the heart's left ventricle through the aorta
The circulatory system carries white blood cells and antibodies to fight against pathogens and infections
The circulatory system helps regulate body temperature by transporting heat from the core to the skin's surface
where it can be released
Metabolic waste
Carbon dioxide
from the cells to the lungs for exhalation
a waste product of cellular respiration
The circulatory system carries carbon dioxide
Nutrients
Oxygen
thin-walled vessels that allow for the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and surrounding tissues
Tiny
preventing backflow
Valves in the heart ensure that blood flows in the correct direction
and capillaries
veins
including arteries
Tubes that carry blood
Function
Definition
and hormones throughout the body
nutrients
oxygen
The circulatory system is a network of organs and vessels that transports blood
Disorders and Diseases of the Circulatory System
Arrhythmias
Blood clots
Stroke
Heart failure
Atherosclerosis
Hypertension
Circulation of Blood
Pulmonary circulation
Exchange of gases
Systemic circulation
Oxygenation of blood
Pathway
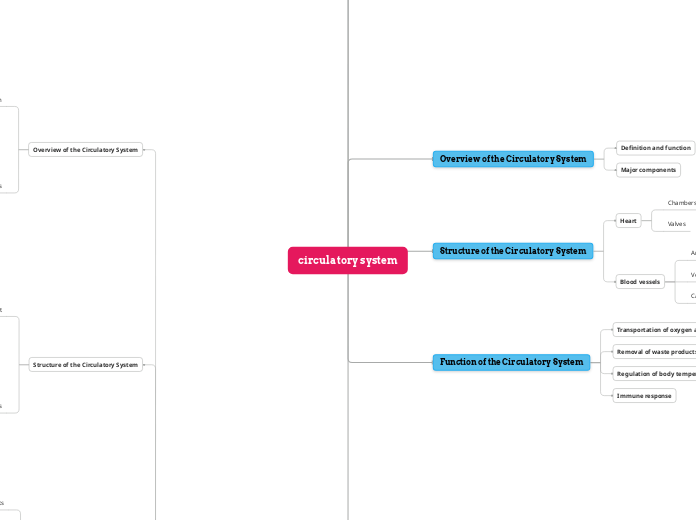
Function of the Circulatory System
Immune response
Regulation of body temperature
Removal of waste products
Transportation of oxygen and nutrients
Structure of the Circulatory System
Blood vessels
Capillaries
Veins
Arteries
Heart
Valves
Chambers
Overview of the Circulatory System
Major components
Definition and function