by paola Hernández Gutiérrez 3 years ago
221
Diálisis
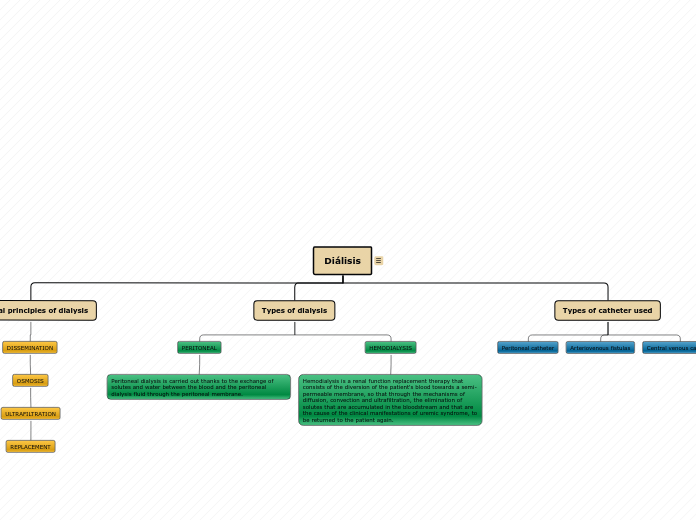
Dialysis is a medical procedure that facilitates blood purification by partially replicating the kidney's functions of removing water and solutes and balancing electrolytes and acids.
by paola Hernández Gutiérrez 3 years ago
221

More like this
Hemodialysis (HD) is an extracorporeal blood purification technique that partially supplies the renal functions of excreting water and solutes, and regulating the acid-base and electrolyte balance. It does not supply endocrine or renal metabolic functions.
It consists of interposing between 2 liquid compartments (blood and dialysis fluid) a semi-permeable membrane. For this, a filter or dialyzer is used
ULTRAFILTRATION
REPLACEMENT