by Alison Young 12 years ago
256
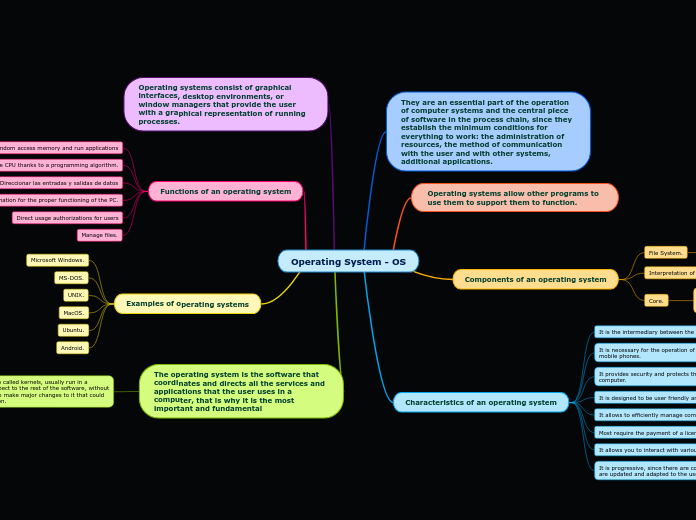
Efavirenz
Efavirenz is primarily used to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase and is administered orally, with increased absorption when taken with a high-fat meal. It has a high protein-binding capacity and can cross the blood-brain barrier, placenta, and breast milk.