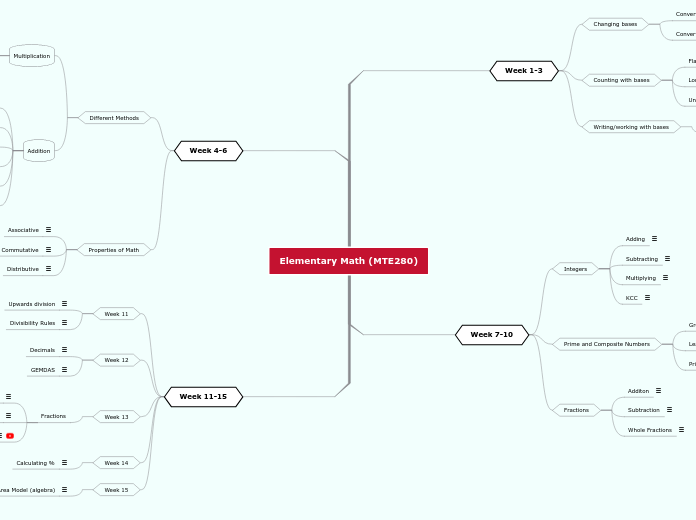
Elementary Math (MTE280)
Week 11-15
Week 15
Area Model (algebra)
- A alternative way to solve multiplication problems where the length and width are used
- Algebra way would be using variables
Ex: 5(32) Ex: Let x=10
5(3x+2)
Week 14
Calculating %
What is 60% of 80?
6 6
X 10 X 8
60 48 = 48%
Week 13
- Simplify the fractions
- Multiply the numerators of the fractions to get the new numerator
- Multiply the denominators of the fractions to get the new denominator.
- When subtracting denominators must be the same
- If they're not the same find the GCF to get the denominators the same
- When adding denominators must be the same
- If they're not the same find the GCF to get the denominators the same
Week 12
GEMDAS
GEMDAS
G- Groups
E- Exponents
M- Multiplication
D- Division
A- Addition
S- Subtraction
- The same as Pemdas but instead of parenthesis use groups, separate groups by addition and subtraction symbols
Decimals
- a fraction whose denominator is a power of ten and whose numerator is expressed by figures placed to the right of a decimal point
- Make sure the decimals are lined up and numbers lined up in the same value
34.5 + 6.32
34.50
+ 6.32
40.82
Week 11
Divisibility Rules
2- End in even number
3- Sum of digits divides into 3
4- Last 2 digits divide into 4
5- Ends in 0 or 5
6- If 2 & 3 work than 6 works
8- last 3 digits divide into 8
9- sum of digits divide into 9
10- ends in 0
Upwards division
- An easier way than long division
Ex:
52
6
52 - 48 = 8 4/6
6
Week 4-6
Properties of Math
Distributive
The distributive property lets you multiply a sum by multiplying each addend separately and then add the products
Ex: 5(7+1)
Commutative
a math rule that says that the order in which we multiply numbers does not change the product
Ex: 5+7+1=1+7+5
Associative
The associative property states that you can add or multiply regardless of how the numbers are grouped
Ex: 5+(7+1)= (5+7)+1
Different Methods
Expanded Form
Allows you to create simpler addition problems and add them together by breaking down one of the factors into smaller numbers
- separates flats, long, and units
Ex: 243
+ 429
+ 200+40+3
400+20+9
600+60+12
= 672
Scratch Method
Cross of the number as you reach the base value you are looking for
- Every time you count up to ten you cross off the number and if there is a reminder you start counting again from that reminder but if there is no number after the reminder the number goes straight down
Ex:
3
6
4 R 3
3
+ 5 R 1
8
2 R 1
1
4
36
The lattice method of addition is an alternative way of adding numbers that eliminates the need to carry tens over to the next column
- Add the digits diagonally
- Ex: 243+429
- 3+9=12
- 4+2=6
- 2+4=6
= 672
Left to Right
An Addition Strategy where you start from the left side of the problem rather than the right side and Switching the order so that we begin with the largest values
- place a zero for the other place numbers when adding
- Ex :
342
+ 156
400
90
8
498
Trade-off
This method is also similar to the friendly numbers, but is wrote down vertically down
- Want to get pairs of factor numbers of 10
- ex: 53 + 78 = 53(-2) + 78(+2) = 131
51
+80
=131
Friendly numbers
an easier way to add by changing numbers to a 0 so changing it to become a factor of 10.
- You subtract from one set of number and add it onto the other to make it a factor of 10
- They are called friendly because once the rule for adding 0 is understood, that understanding can now be used to larger numbers that end in 0
- ex: 36+25 = 36(+4) + 25(-4)
- 40+21= 61
Multiplication
Expanded Model
Allows you to create simpler multiplication problems and add them together by breaking down one of the factors into smaller numbers
- separates flats, long, and units
- Ex: (43)(56)
- (40 + 3) x (50 + 6)
- (40)(50) = 2000
- (50)(3) = 150
- (40)(60) = 240
- (3)(6) = 18
- 2000+150+240+18 = 2408
Area Model
A alternative way to solve multiplication problems where the length and width are used
- A square is drawn out and the one set of numbers is written on top (Horizontally) while the other set is written straight down on the side of the box (vertically)
- Flats, longs, and units are separated in order to simplify
- Ex: (253)(346)
- 200 x 300 = 60,000
- 200 x 40 = 8,000
- 200 x 6 = 1,200
- 50 x 300 = 15,000
- 50 x 40 = 2,000
- 50 x 6 = 300
- 3 x 300 = 900
- 3 x 40 = 120
- 3 x 6 = 18
- (60,000+15,000+900)+(8,000+2,000+120)+(1,200+300+18) = 87,538
Lattice
an alternative way for long multiplication and is a method constructed to fit numbers being multiplied.
- Add the numbers diagonally
- Get to write down the tens first than ones
- answer is read from left to right
Ex:
(26)(38)
Add numbers diagonally in diagram making it equal 988
Week 7-10
Fractions
Whole Fractions
When a numerator and denominator are the same they are considered whole fractions
Ex: 11/11
When adding a whole number and a fraction you can pair them together
Ex: 8+ 5/17
=8 5/17
Subtraction
- When subtracting denominators must be the same
- If they're not the same find the GCF to get the denominators the same
Ex: 7/8- 5/8 = 2/8 (can simplify down)
= 1/4
Additon
- When adding denominators must be the same
- If they're not the same find the GCF to get the denominators the same
Ex: (5) 5/12 + 2/15 (4)
- Get the denominators the same
- When multiplying, multiply both the numerator and denominator
25/60 + 8/60 = 33/66 (simplify)
= 11/20
Prime and Composite Numbers
Prime Factorization
Factor Tree
45= 9x5, 9= 3x3
Factors= 5,3,3
Prime factorization = 3^2 x 5
Upside down division
Least Common Multiple
- The greatest number that two or more numbers are divisible by
Ex: a) 3^2 x 5^4 x 7 b) 2 x 3^7 x 5^2 x 11
GCF: 3^2 x 5^2
LCM: 2 x 3^7 x 5^4 x 7 x 11
Greatest Common Factor
- The smallest number that goes into two or more numbers
- When factorizing use the small numbers, only use the same numbers and use the lowest exponent
Ex: 18= (1x18),(2x9), (3x6)
GCF=6
Integers
KCC
Keep Change Change
K C C
3 -(-4)
3+(+4)
= 7
Multiplying
When the signs are the same the answer is positive
When the signs are the opposite the answer is negative
10 (-15)
+ -
= -150
(-7)(-20)
- -
= 140
Subtracting
7-4
+++++++
- The red indicates 4 being taken away from the 7 positives
Adding
5+(-3)
+++++
---
- The green and red indicate the Zero bank meaning there is 2 positives left over
Week 1-3
Writing/working with bases
Addition
12 base five + 22 base five
(.....)(.....).. + (.....)(.....)(.....)(.....)..
22 + 42 = 64 base five
- In order to use addition you have to fine the base five of each number first. You get 2 longs and 2 units for 12 base five making it equal to 22. You get 4 longs and 2 units for 22 base five making it equal to 42. You then have to add 22+42 to get 64 base five.
Counting with bases
Units
Units: the number of individual units
- Units are the last number when putting together the number if there are 2 flats and 5 longs and 7 units the number would be 257
Longs
Longs: a collection of units, depending on the base that is how many units will make up a long
- Ex; base five means 5 units will make a long
- Longs are the middle number when putting together the number if there are 2 flats and 5 longs the number is 250
Flats
Flats: A collection of longs depending on the base that is how many longs will be in a flat
- Ex; Base five there will be five longs in a flat
- Flats are the first numbers when putting together a number if there are 2 flats than the number is 200
Changing bases
Convert to base 5
Convert to base 5 : 8
(.....) ... = 13 basefive
- Since we are converting to base five using 8 there is only one long because since it is base five only 5 could fit into a long and there are 3 left over making it 13.
Convert to base 10
Convert to base ten: 23 five
(.....)(.....) ...
5 + 5 + 3 = 13
- In order to convert to base 10 with 23 base five you have to put 2 longs and 3 units each long is equal to five since the base is five and there are only 3 units.