DDI
Enzyme inducers:
Increase metabolism of Rufinamide due to induction of carboxylates
Valproic acid increases rufinamide concentrations through unknown mechanisms
Inducers/Inhibitors of UGT
Lamotrigine
Ezogabine
CYP3A4 Inducers:
Reduce half-life and plasma conc. of:
-Zonisamide
Can decrease the exposure of:
-Ethosuximide
-Tiagabine
Inducers/Inhibitors/Etc.
Inhibitors
CYP2C9
CBD/Cannabidiol
Valproic acid: +UGT/epoxide hydrolase
Inducers
CYP2C9, CYP3A, UGT
Carbamazepine: +CYP1A2
-Phenytoin
-Phenobarbital
-Primidone
Metabolism
No Metabolism
-Gabapentin
-Pregabalin
-Vigabatrin
-Levetiracetam
CYP3A4
CBD: +CYP2C19, UGT
CYP3A
-Perampanel
N-Glucuronidation
-Lamotrigine
-Ezogabine
Note:
Drugs that induce or inhibit UGT can alter the metabolism of both of them
Mnemonic: eating GLUCose every day makes you LAzy EAZILY. Understand Glucose To prevent this.
-GLUC = Glucuronidation
-LA = LAmotrigine
-EAZILY = EZogabine
-UGT = Understand Glucose To
Emmitte Anti-Seizure Drugs
Misc.
Stiripentol
ADME:
~Used in combo with clobazam in Dravet syndrome
~Increases GABA lvls in neuronal tissue
~Highly protein bound
~Inc. plasma conc. of clobazam via inhibition of CYP3A4 & CYP2C19
Cannabidiol
ADME:
~Cannabis sativa, no psychoactive THC
~CBD metabolized by CYP2C19, CYP3A4, UGT enzymes
~Inhibitor of CYP2C19
Perampanel
ADME:
~highly protein bound
~metabolized by CYP3A
Txt: partial seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures
1st in class anti-seizure drug due to being highly selective
Example of successful target-based drug design
Ezogabine
ADME:
~acts on K channels
~metabolic pathway is N-glucuronidation by UGT (anti-seizure drugs that induce or inhibit UGT can alter metabolism)
~80% protein bound
Rufinamide
ADME:
~major metabolite due to carboxylesterase-medziated hydrolysis
~low protein binding
~enzyme inducing anti-seizure drugs increases metabolism due to induction of carboxylesterases
~valproic acid increase conc. by 70%, DDI
~food increases oral absorption/solubility of drug
Lacosamide
ADME:
~Synthetic derivative of D-serine
~converted via CYP2C19
~No effect on P450s/no DDI w/ other anti-seizure drugs
Zonisamide
ADME:
~Sulfonamide derivative
~CYP3A4 inducers (i.e. phony/carb) will alter PK -> reduce half-life + plasma conc.
~50% excreted as glucuronide conjugate SMAP, byproduct of CYP3A4 metabolism
Contradindicated in pts. allergic to sulfonamides.
Levetriacetam, Brivaracetam
ADME:
~rapid + complete absorption
~min. protein binding, NOT metabolized by UGT/CYP450/epoxide hydrolase
~binds synaptic vesicle protein CV2A
~Brivaracetam introduced w/ increased affinity for SV2A + Na channel blocking
Topiramate
ADME:
~70-80% excreted unchanged renally, dose reduction req. for renal insufficiency
~Exhibits polypharmacology = broad spectrum anti-seizure activity
Lamotrigine
ADME:
~Blocks Na ion channels
~metabolized by N-glucuronidation + DDIs w/ drugs that induce or inhibit UGT
Monotherapy of variety of seizures, incl. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Felbamate
~34 cases of aplastic anemia (!3 ☠️) and 23 cases of hepatic failure (5 ☠️)
~Black box label warning
Valproic Acid
ADME:
~Highly protein bound
~INHIBITOR of CYP2C9, UGT, epoxide hydrolase
~2-propyl-4-pentenoic acid is toxic metabolite
Teratogenic + rare but potentially fatal hepatotoxicity
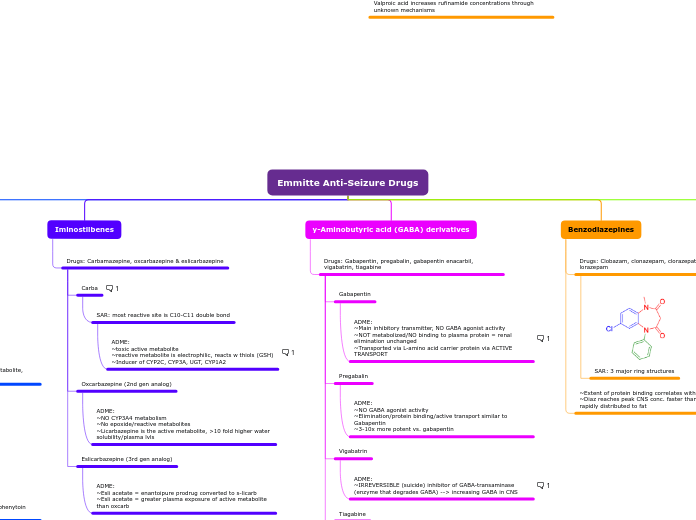
Benzodiazepines
~Extent of protein binding correlates with lipid solubility
~Diaz reaches peak CNS conc. faster than Loraz but is more rapidly distributed to fat
Drugs: Clobazam, clonazepam, clorazepate, diazepam, lorazepam
Diazepam+Lorazepam used IV or IM for status epilepticus
Rest used orally in chronic therapy
SAR: 3 major ring structures
y-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) derivatives
Drugs: Gabapentin, pregabalin, gabapentin enacarbil, vigabatrin, tiagabine
Tiagabine
ADME:
~Highly protein bound
~Oxidation by CYP3A4 --> CYP3A4 inducers reduce exposure
~Increased potency at GABA transporter
Vigabatrin
ADME:
~IRREVERSIBLE (suicide) inhibitor of GABA-transaminase (enzyme that degrades GABA) --> increasing GABA in CNS
Concet. dependent progressive + permanent bilateral VISION LOSS in high % of pts. Restricted availability (SHARE program) and periodic vision testing is req.
Pregabalin
ADME:
~NO GABA agonist activity
~Elimination/protein binding/active transport similar to Gabapentin
~3-10x more potent vs. gabapentin
Gabapentin
ADME:
~Main inhibitory transmitter, NO GABA agonist activity
~NOT metabolized/NO binding to plasma protein = renal elimination unchanged
~Transported via L-amino acid carrier protein via ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Gabapentin encarbil is a prodrug which overcomes absorption issues related to gabapentin
Iminostilbenes
Drugs: Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine & eslicarbazepine
Eslicarbazepine (3rd gen analog)
ADME:
~Esli acetate = enantoipure prodrug converted to s-licarb
~Esli acetate = greater plasma exposure of active metabolite than oxcarb
Oxcarbazepine (2nd gen analog)
ADME:
~NO CYP3A4 metabolism
~No epoxide/reactive metabolites
~Licarbazepine is the active metabolite, >10 fold higher water solubility/plasma lvls
Carba
Causes idiosyncratic toxicity known as Anticonvulsant Hypersensitivity Syndrome (ACHS) indicated by fever, rash, hepatotoxicity
SAR: most reactive site is C10-C11 double bond
ADME:
~toxic active metabolite
~reactive metabolite is electrophilic, reacts w thiols (GSH)
~Inducer of CYP2C, CYP3A, UGT, CYP1A2
Most cars fit 4 passengers (4 inducers)
Barbiturates & drugs derived from barbiturates
succinamides
Blockade of T-type Ca2+ Channel
Drugs: ethosuximide
Absence seizures
ADME:
~NOT an enzyme inducer
~CYP3A4 inducers decrease exposure bc it converts it to inactive
Hydantoins
Inactivation of Na+ channel
Drugs: Phenytoin & fosphenytoin
ADME:
~90% Protein bound
~Non-linear PK AKA metabolic route is saturable
~Induces CYP2C, CYP3A, & UGT
~High pH + cannot be diluted for infusion --> fosphenytoin prodrug for injection via IM/IV
Subtopic
Barbiturates
MOA: Increase GABA activity
Drugs: Phenobarbital & Primidone
ADME:
~Inducers of CYP2C, CYP3A, UGT
~Pheno: low LogP -> SLOW onset -> LONG DOA
~Prim: Produces either pheno or PEMA (major metabolite, weaker anticonvulsant, more toxicity)