The turning of the rod does activate
catalytic sites in the knob though. These make ATP from ADP and phosphate groups.
The rotor's spinning makes an internal rod
spin. This rod is connected to a knob that is only stopped from spinning by the stator which holds it in place.
After the rotation the protons enter the
stator again but through a different channel which deposits them into the mitochondrial matrix.
The protons are then entered into the
rotor which they connect to and do a full
rotation around.
Protons go down their gradient
and enter a channel of the stator part of ATP Synthase.
The electrons from NADH/FADH2
move along four complexes in order
of increasing electronegativity whilst
releasing energy. This occurs on the
inner mitochondrial membrane.
These complexes pump
protons (H+) through
the mitochondrial membrane
into the intermembrane
space. These are used in
Chemiosmosis to produce
ATP.
photophosphorylation is making ATP by adding a phosphate group to ADP
Cytochromes are proteins
that differ by their heme
groups which carry electrons
down the chain.
Throughout complex III
the electrons are passed
through mainly cytochromes.
Ubiquinone is not a protein but
moves within the membrane and
transfers electrons from I and II
into protein complex III.
Ubiquinone (Q)
Protein Complex III
Cytochromes (Cyt)
Cyt b
Fe-S
Cyt c1
Cyt c
Protein Complex IV
Cyt a
Cyt a3
This is the last electron
carrier in the ETC. The
electrons are then passed
onto Oxygen in the
mitochondrial matrix.
Oxygen
Two Hydrogen Atoms
are then binded to
Oxygen to create H2O.
The final redox reaction in the cycle
happens when Malate is oxidized and becomes oxaoacetate like at the beginning of the cycle. NAD+ is also reduced to NADH.
A water molecule combines with the
Fumarate to form Malate.
Step 8
Since 2 Acetyl Coenzyme A are produced
in Pyruvate Oxidation the products of the Citric Acid Cycle per glucose are 6 NADH, 2FADH2, and 2 ATP.
A redox reaction occurs and Succinate is oxidized, becoming Fumarate. FAD is reduced to FADH2 from this process as well.
The CoA unbinds and is replaced with a phosphate group. This process creates GTP or ATP depending on the type of cell. In most animal cells GTP is made and used to make ATP. In plant cells and some animal cells ATP is directly produced. When the CoA and phosphates are swapped Succinate is produced.
Another redox reaction occurs and
as a second molecule of CO2 is released another NAD+ is reduced to NADH. A CoA then binds with the resulting succiynl to form succinyl CoA.
Through a redox reaction the isocitrate
is oxidized to become the five carbon a-Ketoglutarate. In this reaction a molecule of CO2 is released and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
Citrate is dehydrated and through
rehydration is converted into Isocitrate.
Citrate is produced through the
addition of Acetyl CoA's two carbon
group to oxaloacetate's four carbon
group.
after signal molecule is received inside the cell Transduction takes place
TRANSDUCTION: the sequential activation of KINASES, by getting phosphates from ATP
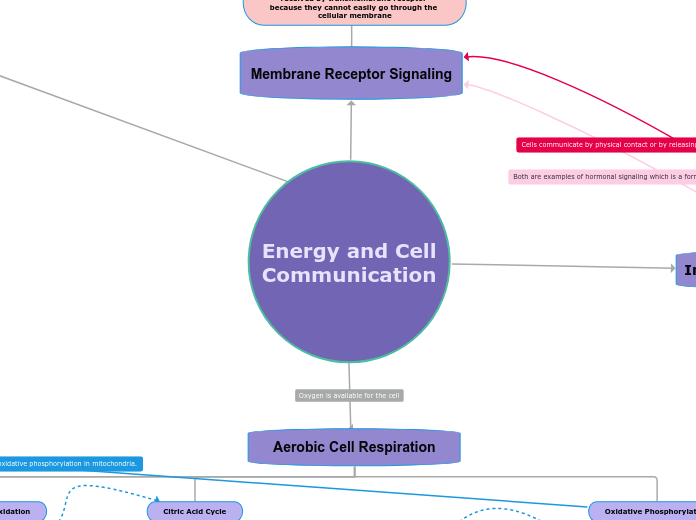
Large and polar signal molecules must be received by transmembrane receptor because they cannot easily go through the cellular membrane
Energy payoff
Energy investment
Net 2 NADH
Net of 2 ATP & 2 NADH
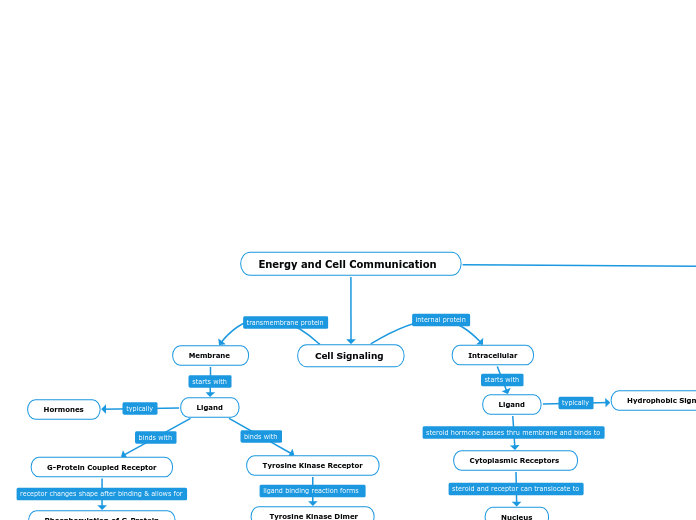
Energy and Cell Communication
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
6 CO2 + 6H2O + LIGHT -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Located in the CHLOROPLAST
STAGE 2: Calvin Cycle (stroma)
3 PHASES
PHASE 3
REGENERATION OF CO2 RECEPTOR
5 of the G3P molecules go on to form more ribulose bis phosphate ( the carbon acceptor) and 1 molecule of G3P leaves the cycle to form glucose and other sugars.
PHASE 2
REDUCTION
Using 2 ATP and 6 NADPH, forms molecules of G3P
PHASE 1
CARBON FIXATION
CO2 from the atmosphere is added to ribulose bisphosphate using RUBISCO. This forms a 6-carbon unstable intermediate.
The short intermediate then splits to 2 molecules of 3 carbon (3-phosphoglycerate). This is the first stable molecule.
STAGE 1: Light Reaction (thylakoid membrane)
Photosystem I
photon of light absorbed by one pigment molecule causing electrons to be excited
as they go back to the ground state energy is released which eventually reaches the main chlorophyll a molecules (P700).
Electrons of these chlorophyll a molecules jump to the excited state and are grabbed by a primary electron acceptor.
electrons go to Ferridoxin (Fd) then on to NADP+ to form NADPH
The electron hole in P700 chlorophyll molecules is supplied from electrons coming down the electron transport chain
This transfer of electrons down the electron transport chain lead to formation of ATP by photophosphorylation.
THIS IS THE NON-CYCLIC FLOW OF ELECTRONS
CYCLIC FLOW: when there is excess NADPH, only PSI is used. ATP is made by phosphorylation. No NADPH is formed.
Photosystem II
photon of light is absorbed by chlorophyll, this absorbed energy causes electrons to jump to excited state
then go back down to the ground state releasing the energy
energy is transferred from one pigment molecule to the other, eventually reaching the main pair of chlorophyll a molecules (P680)
the electrons are grabbed by an acceptor molecule
The electron hole in the main chlorophyll a molecules is constantly fed by electrons released when water is split. O2 is released
Electrons from the primary electron acceptor then go down an electron transport chain eventually reaching chlorophyll a molecules of PS1
Intracellular Signaling
Reception
Steps
Step 5: The mRNA is translated by ribosomes into a specific protein. This process brings about gene expression.
Step 4: The bound protein acts as a transcription factor, stimulating the transcription of the gene into mRNA.
Step 3: The hormone-receptor complex has the right configuration to enter the nucleus through a nuclear pore and binds to specific genes.
Step 2: The signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein in the cytoplasm, activating it. This forms a hormone-receptor complex.
Step 1: A small nonpolar signaling molecule such as a hormone passes through the cell (plasma) membrane.
The binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor protein
Receptor
Present in a target cell that receives the signal molecule. Intracellular signaling receptors are located in the cytoplasm.
Signaling Molecule/Signal/Ligand
Molecule released by a cell which is received by another cell. The signaling molecules that use intracellular signaling are small nonpolar molecules such as hormones that can pass through the hydrophobic region of the phospholipid bilayer that makes up cell membranes.
Membrane Receptor Signaling
TYPES OF FIRST MESENGER RECEPTORS
ION CHANNEL
signal molecule binds to litigated protein causing it to open
TYROSINE KINASE
consist of 2 polypeptides that dimerize when a signal molecule binds to them.
the polypeptides become kinases (they add phosphates to proteins)
Once all 6 get phosphate groups they become ACTIVE
G-PROTEIN COUPLED (GCPR)
FIRST: Signal molecule actives the receptor when it binds to the G-protein
SECOND: This binding slightly changes the shape of of the GCPR and this allows the G-protein to bind to it
NEXT: GDP gets replaced with GTP activating it and it slides down the membrane to active enzyme and its GTP becomes GDP again
Aerobic Cell Respiration
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the process
in which H+ is converted to
ATP. This begins when H+
interacts with an enzyme
called ATP synthase.
ATP Synthase
Part 5
Part 4
Part 3
Part 2
Part 1
Electron Transport Chain
Protein Complex II
The electrons from
FADH2 are transferred
to a lower level of the
electron chain at
Complex II resulting in
about 1/3 the energy
for ATP synthesis
compared to NADH.
Iron-Sulfur Protein (Fe-S)
A redox reaction occurs and
the electrons are passed to
Ubiquinone.
Protein Complex I
The electrons from NADH are
transferred to a molecule of
Flavoprotein.
Flavoprotein (FMN)
A redox reaction occurs and
Flavoprotein passes the electrons
to an Iron-Sulfur Protein.
Iron-Sulfur Protien (Fe-S)
A redox reaction occurs and
the electrons are passed to
Ubiquinone.
Citric Acid Cycle
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Pyruvate Oxidation
2 Acetyl Coenzyme A
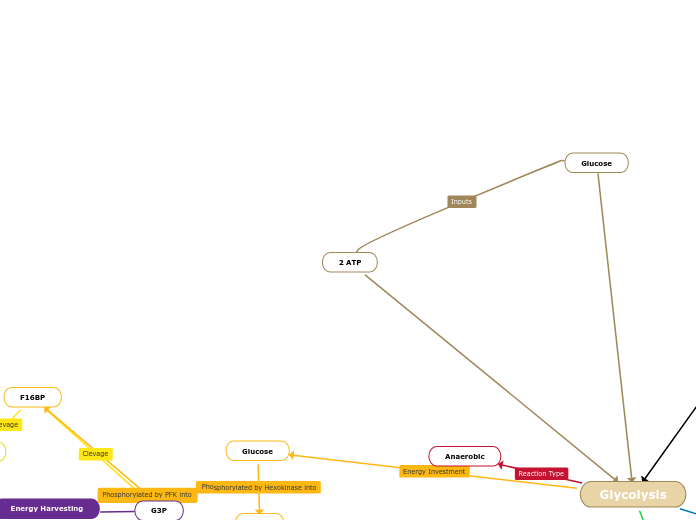
Glycolysis
Occurs outside the mitochondria in the cytosol and breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules through substrate-level ATP synthesizing.
Involves
- energy investment
- energy payoff
Glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate
Fructose 6 phosphate
Fructose 1,6-biphosphate
2 pyruvate