Learning Communities
Composition credits
Humanities credits
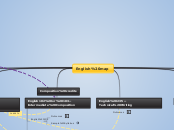
English map
English--Literature
Requires English 101
English 264-5--English Literature
English 262--Children's Literature
English 261--Bible as Literature
English& 246--American Literature III
English& 245--American Literature II
English& 244--American Literature I
English 234, 242, 271, 280
English 220 --Introduction to Shakespeare
English--Creative Writing
Englsh 279
English 278
English 276, 278, 279
English 235--Technical Writing
Upon satisfactory completion of the course, students will be able to:
1. Develop an understanding of the nature and substance of technical reports.
2. Develop an understanding of the qualities and elements that go into good business and science reports.
3. Organize and prepare various types of technical writing, including reports, technical descriptions, proposals, and feasibility studies.
4. Use current technology to gather, evaluate, and analyze information.
5. Write clearly, effectively, and concisely.
English102 or 103--Intermediate Composition
English 103
Upon successful completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- Study works representing the genres of fiction, the short story, poetry, and drama to analyze the main elements of each. PLO: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Consider the cultural, moral, and aesthetic values a work reflects and to evaluate them in light of one’s own values. PLO: 3
- Read literature that reflects a variety of ethnic backgrounds and cultures. PLO: 3
- Demonstrate proficiency with the objectives of English 101; particular attention should be given to style. PLO: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
English 102
Upon successful completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- Develop further proficiency in English 101 skills. PLO: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Analyze and evaluate the skeleton of an argument – proposition, main issues and supporting evidence. PLO: 3
- Recognize and assess audience profiles for arguments. PLO: 3
- Recognize and assess the writer’s commitment to issues and test whether such attachment has a rational basis. PLO: 3, 4
- Assess the evidence provided for an argument – its factual strength, authoritative support, logical validity, relevance to the proposition, etc. PLO: 3, 4
- Detect and evaluate non-argumentative persuasive techniques – rhetorical devices such as irony, satire, anecdotal evidence, flattery and analogies, and logical fallacies – used to sway readers’ emotions. PLO: 3, 4
- Use library research skills in electronic, print, and other sources to gather support for arguments. PLO: 4
- Recognize that different academic disciplines may rely on different kinds of arguments and assess what types of argument and evidence are appropriate for different fields of knowledge. PLO: 3
- Write arguments appropriate to audience, occasion and discipline. PLO: 4
- Participate in collaborative projects. PLO: 5
English 101-- Beg. College-level Composition
Sample Syllabus
Course Map
Outcomes
Theme-based
Pre-College
I-Best
ALP (101 with support)
English 95
English 85
ABE
Language Learners
EAP
AESL