by Guzal Kamariddinova 2 years ago
136
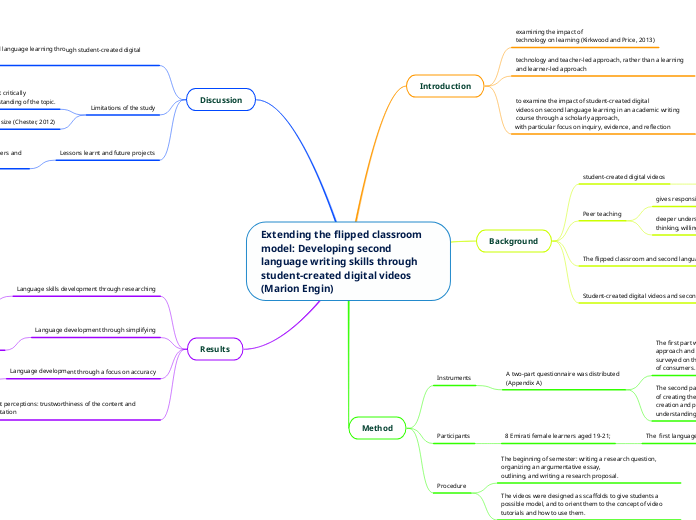
Extending the flipped classroom model: Developing second language writing skills through student-created digital videos (Marion Engin)
The study investigates the influence of student-created digital videos on second language acquisition within an academic writing course, emphasizing a flipped classroom model. It aims to shift the focus from traditional teacher-led methods to a more learner-centered approach.