6°F: -Badillo Emiliano. -Díaz Andrea Mariana. - Díaz Silva Hugo. - Lopez Frida Yareli. - Gutierrez Lizeth Alejandra. - Mendoza Zuleica Yhardel. - Santana Santiago. 18 de febrero del 2021.
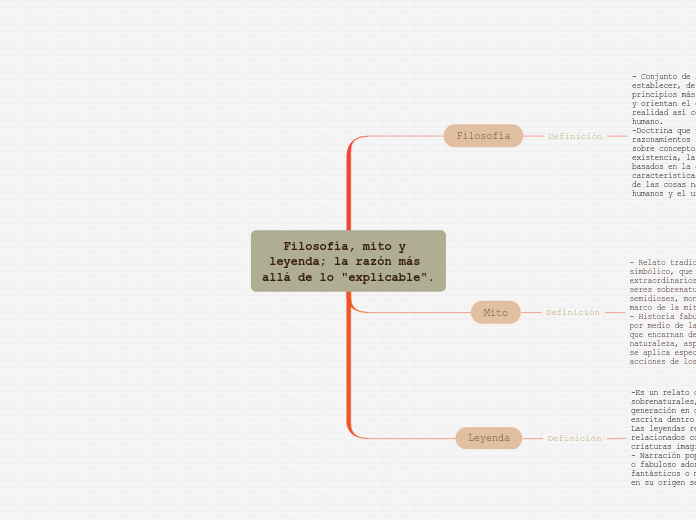
Filosofía, mito y leyenda; la razón más allá de lo "explicable".
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
Leyenda
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
-Es un relato que cuenta hechos humanos o sobrenaturales, que se transmite de generación en generación de manera oral o escrita dentro de una familia, clan o pueblo. Las leyendas relatan hechos y sucesos relacionados con la patria, héroes populares, criaturas imaginarias y ánimas. - Narración popular que cuenta un hecho real o fabuloso adornado con elementos
fantásticos o maravillosos del folclore, que en su origen se transmite de forma oral.
Try answering these questions in order for you to come up with a closure:
- Have all problems been solved?
- Is it clear what happens with all your characters in the story?
- Has the challenged transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
El conocimiento de la leyenda sirve para conocer antecedentes culturales y espirituales
así como mayor enriquecimiento culturas y literario, así mismo se fomentan los valores
patrios en la sociedad.
Mito
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
There wouldn't be any tension and excitement in your story if there weren't any obstacles in your character's way.
- Relato tradicional, sagrado, dotado de carácter simbólico, que usualmente relata acontecimientos extraordinarios y trascendentes involucrando a seres sobrenaturales o fantásticos (como dioses o semidioses, monstruos, etc) y que funcionan en el marco de la mitología. - Historia fabulosa de tradición oral que explica, por medio de la narración, las acciones de seres que encarnan de forma simbólica fuerzas de la naturaleza, aspectos de la condición humana, etc.; se aplica especialmente a la que narra las acciones de los dioses o héroes de la Antigüedad.
A story is nothing more than a character overcoming a series of difficulties to reach the desired goal. Obstacles usually create suspense and conflict. In overcoming obstacles, there is growth: weak becomes strong; hatred turns into love; sadness into happiness; wrong into right; lies into truth; or evil becomes good.
See a few examples below:
- stopping a meteor
- finding a killer
- finding love
El conocimiento de un mito permite que las personas tengan un mejor conocimiento o comprensión de los distintos planos de la realidad.
Mito vs leyenda
Leyenda: - Resalta alguna característica de un
pueblo o lugar.
- Los lugares donde se desarrolla la historia son: ciudades o pueblos definidos.
- Los personajes que se usan al momento de contar la historia son héroes, gente común, seres
sobrenaturales o del inframundo. Mito: - Explica lo sobrenatural o el origen de
algo.
- Sus lugares son: geografía indefinida anterior a la moderna.
- Dioses, héroes, semidioses, monstruos.
Filosofía
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Definición
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
- Conjunto de saberes que busca establecer, de manera racional, los principios más generales que organizan y orientan el conocimiento de la realidad así como el sentido del obrar humano. -Doctrina que usa un conjunto de razonamientos lógicos y metódicos sobre conceptos abstractos como la existencia, la verdad y la ética basados en la ciencia, las características y las causas y efectos de las cosas naturales como el ser humanos y el universo.
Type in the name of your character.
En la vida cotidiana
Add other properties of the character.
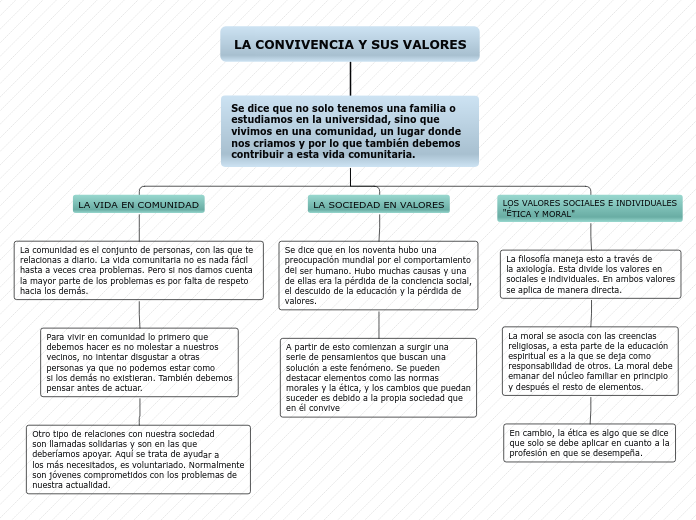
La filosofía cumple un papel principal en la cultura de hoy, es la base fundamental de todas
las creaciones humana y es llamada "la madre de todas las ciencias". Ayuda a entender las dificultades, ventajas, desventajas de nuestro propio ser. En si es un conjunto de pensamientos, críticas y teorías de la humanidad.
Filosofía vs mito
La filosofía se basa en hechos reales, comprobados, concretos y naturales. Es
contundente y racional, se desarrolla en un mundo actual. No narra sucesos, los
explica con ciencia, y no busca ser modelo para los hombres.
Mientras que el mito existe la “inspiración divina”, se basa en lo extraordinario, sobrenatural e imprescindible, es ambiguo y contradictorio, se desarrolla en un tiempo donde el mundo no tiene su forma actual mientras que narra sucesos para
los hombres verdaderos o falsos, los cuales tienen que ser un modelo para los hombres.