by maira trujillo 1 year ago
118
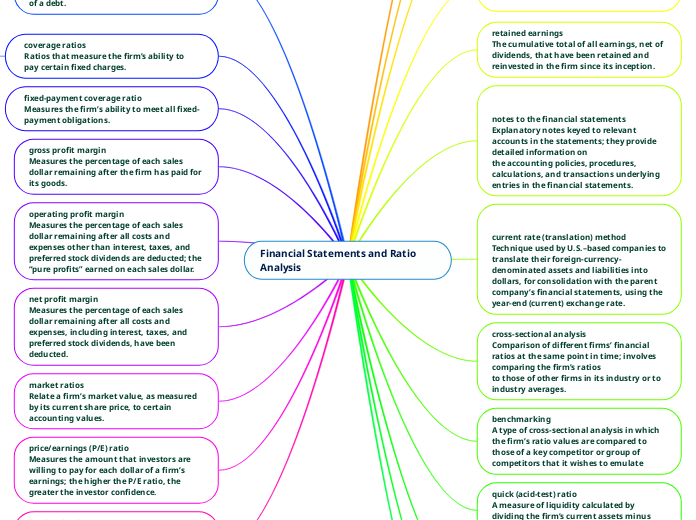
Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis
Financial statements offer a comprehensive overview of a firm's financial health through various measures and ratios. Gross profit margin and net profit margin are essential indicators of profitability, showing how much of each sales dollar remains after covering costs.