by Nurul Aqila 8 years ago
447
Food Emulsifier
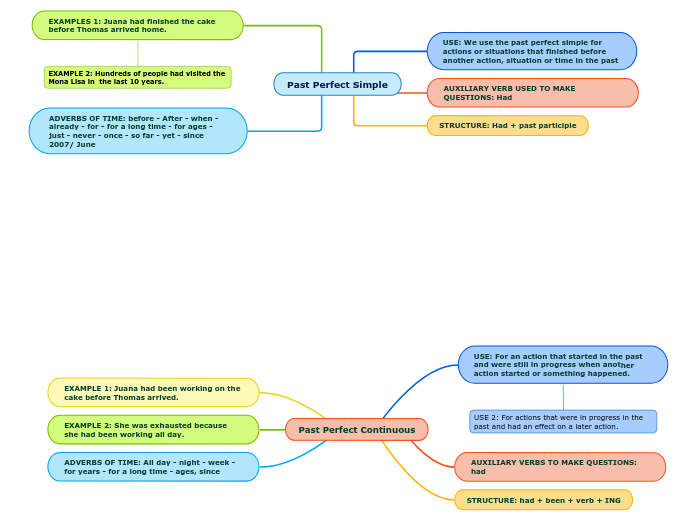
Emulsifiers are essential for stabilizing mixtures of oil and water by reducing surface tension and interfacial energy, thus preventing separation. These agents possess both hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads, allowing them to orient at the phase interface.