Response To Exercise
Define: physiological response is the bodies automatic response to a stimulus.
training: aerobic training can decrease heart rate at rest and increase stroke volume during some workloads.
age: due to size, younger children have a lower stroke volume but as we get older the stroke volume increases. same with heart rate.
stroke volume: the count of blood ejected per beat by the left ventricle into the aorta.
Physiological Response
Effects
Long Term
stroke volume at rest is higher in a trained person rather than untrained. it can pump more blood per minute increasing cardiac output when exercising
cardiac hypertrophy: heart increases in size and wall of left ventricle gets thicker.
increase blood volume and blood plasma increase in strength to tendons and ligaments
Short Term
increase in heart rate and stroke volume
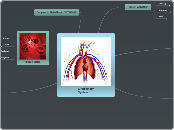
increase carbon dioxide removal and increase in lactic acid production
increase oxygen intake for muscle movement
Factors
duration
intensity
frequency