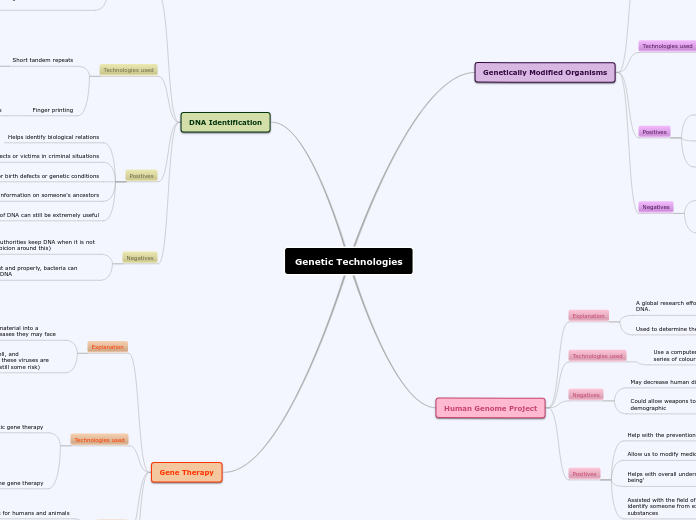
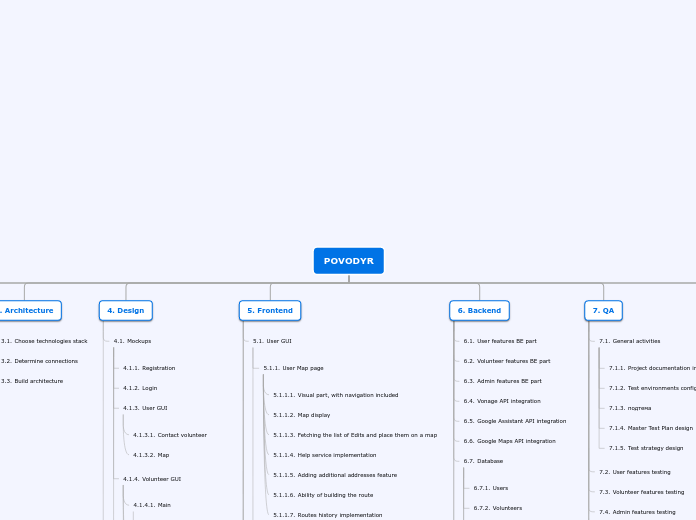
Genetic Technologies
Gene Therapy
Seen as unethical by many people as it is 'playing God'
Could lead to cancer since there is a
possibility of disrupting gene regulation
Some viral vectors could infect a broader
range of cells than intended
Successful germ line therapy leads to the possibility of eliminating select diseases from a certain family of people
Treats diseases for humans and animals
Germ-line gene therapy
The result of this is permanent changes that are passed down to further generations
Somatic gene therapy
Is safer approach because it affects only the targeted cells in the patient, and is not passed on to future generations
in vivo
The gene is transferred to cells inside
the host's body
ex vivo
Cells are changed outside of the body and
transplanted back in
Vectors are used to deliver a gene to a cell, and
vectors are commonly viruses. Although, these viruses are changed to be safe for humans (there is still some risk)
Technology involves introducing genetic material into a person's cells to help fight or prevent diseases they may face
DNA Identification
If samples are not stored fast and properly, bacteria can attack the cells that contain DNA
Seen as unethical as some authorities keep DNA when it is not needed (there is a lot of suspicion around this)
Extremely small amounts of DNA can still be extremely useful
Find out information on someone's ancestors
Can test for birth defects or genetic conditions
Identifies suspects or victims in criminal situations
Helps identify biological relations
Finger printing
Often used in criminal cases
Short tandem repeats
Process includes collecting the sample of DNA
(blood tests, mouth swabs, body tissue, semen),
then extracting the DNA from the nucleus of the cell,
copying the DNA, determining the size of the DNA and
finally seeing if the sample matches with another sample
regions of non-coding DNA that have
repeats of the same nucleotide sequence
There are 3 types of testing; parental, forensic and genetic. All of these look for similarities in the genetic markers between 2 samples
DNA identification is a method used to identify a person.
Human Genome Project
Assisted with the field of forensics, as it easier to positively
identify someone from extremely small pieces of biological substances
Helps with overall understanding of the 'blueprint for a human being'
Allow us to modify medicine and make it more effective
Help with the prevention and identification of diseases
Could allow weapons to be created that target the population's demographic
May decrease human diversity
Use a computer that shows the human DNA sequence as a series of coloured bands and each colour represents a base.
Used to determine the 3 billion different nitrogenous bases
A global research effort to identify the 30,000 genes in human DNA.
Genetically Modified Organisms
Negatives
Possible threat to the environment since GMO's are not natural, therefor they clash with the idea of natural growth within the environment
Seen as unethical within society as it is unnatural and still
being explored/researched.
Positives
Benefits the environment
due to decreased use of pesticides.
Allows herbicides to be more
effective on our crops
Allows our crops to not be
as vulnerable to insects
Technologies used
Insertion through vectors
Agrobacterium tumefaciens's tumour production region
causes unctrollable tumour growth when inserted into a plant.
Gene gun
Shooting microscopic pellets of gold/tungsten
that are coated in the DNA being transferred
through a particle gun. The specialized bullet
becomes coated with the pellets once fired,
allowing for the pellets to enter the cell at high
speed. Then, cells are grown on a dish if successful.
Explanation
Genetic modification technology
allows genes to be transferred for
acquiring specific traits using laboratory
techniques
The technology is called Recombinant DNA Technology
The transfer of genes is possible and easy due to
the fact that most life forms share the same language
of heredity or 'DNA code'.