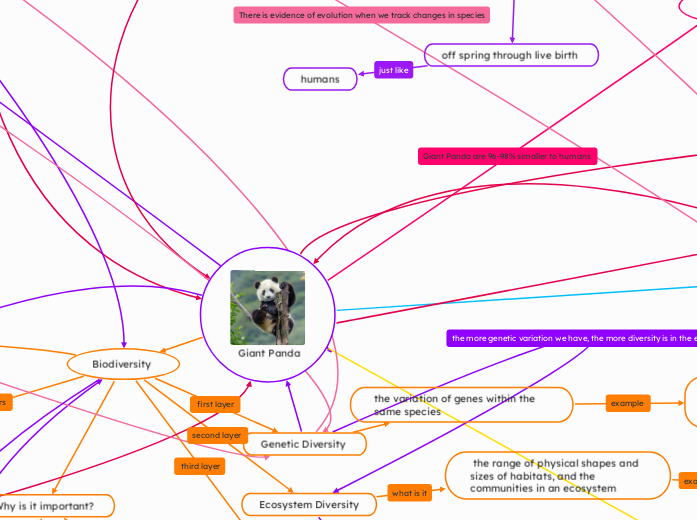
Giant Panda
Plants
Effect of Temperature on Seed Germination
Good Germination (Young Shoots and Roots Present)
Little or No Germination in Most Seeds
photosynthesis
produces oxygen as a byproduct, which is importance for most life on Earth, and helps regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose
carbon dioxide molecules
air
light energy
chloroplasts
Green leaf or stem cells
sun
molecules are split
oxygen ions
oxygen molecules
hydrogen ions
Glocouse molecules
growth, reproduction and metabolic activities.
Plant Evolution
Adaptations to Terrestrial Conditions
Leaves
Cuticle
Seeds
Roots
Stem
Transition from Water to Land
Trends in Kingdom Plantae
Primary Producers in Food Chains
Utilize Visible Light for Photosynthesis
Eukaryotic
Autotrophic
Cell Wall
Alternation of Generations (reproduction)
Photosynthesis
Trends Across All Kingdoms
Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic
Aquatic
Terrestrial
Unicellular
Multicellular
Specialized Organelles
Specialized Organs/Body Systems:
Effect of Water on Seed Germination
Some Seeds Germinate, Roots Rotting
No Germination, No Change
Started to Germinate
Roots shriveling
Germinating and Thriving
Systems
Circulatory System
Blood vessels
Veins
Vinules
Capilaeries
Arteries
Arterioles
Vasodilation
vasoconstriction
diameter
blood flow
Blood
platelet
plasma
White blood Cells
red blood cells
They are adapted to transport oxygen in high-altitude, low-oxygen environments efficiently.
Hemoglobin
have a higher affinity for oxygen to maximize uptake in thin air.
Materials
Hormones
Nutrients
lipids
carbohydrate(glocouse)
protien
The Heart
Heart Rate
Average resting heart rate
60-100 beats per minute.
Lower resting heart rate
to lower metabolic rate.
Valves
Atrioventricular valves
Semilunar valves
vessels
pulmonary Arteries
Superior and inferior vena Cava
pulmonary veins
Aorta
chamers
Atrium
left Atrium
Right Atrium
Vintricles
left vintricle
Right vintricle
Digestive system
4 Major funcation
GI tract
mouth
stomach
Less acidic environment compared to humans, as bamboo does not require strong acids for initial breakdown.
Gastoesphageal Sphincter
small intestine
large intestine
symbiotic bacteria
aid in breaking down cellulose
water
vitamens
colon
cecum
rectum
waste
anus
liver
storage
bile
gal bladder
Detoxification
alcohol and toxins
Jejunum
ileum
villi
pyloric sphincter
liquids
Enzyms
duodenum
pancreas
pancreas juice
a base
lipase
pepsin
Amylase
mucus
stomach acid
ingestion
food
esophagus
peritalsis
chemicaly
saliva
Mainly lubricates food, minimal enzyme activity
salivary glands
mechinically
teeth and tongue
digestion
absorption
egestion
body waste
Respiratory system
Human and Giant Panda respiratory system is the same because we are both mammals
Respiratory Rate
humans
Giant Panda
Gas Exchange
Body Cells
Oxygen
low temperatures
Carbon Dioxide
ventilation
Exhalation
automatic
Inhalation
process
Nose
Mouth
pharynx ( Throat)
Giant Panda has a shared pathway for both food and air.
Trachea
simlair structure
to support its vocalizations and breathing needs.
Lungs
large lunges capacity
to support its large body size and to sustain its energy needs.
Bronchi
Alveoli
Numerous, adapted for lower metabolic rate
cellular respiration
energy
Biodiversity
Taxonomy
Levels
Life
Domain
Kingdom
Pylum
Class
Aves, chonfdrichthyes, osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia and Mammalia.
bony fish
turtles, snakes and lizards
mammals
birds
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Organisims
prokaryotic
bacteria
modern bacteria
extreme environment
eukaryotic
fungi
Mushrooms, yeast and molds
phyla
Division Bryophyta
Division Pteridophyta
Division Coniferophyta
Division Anthophyta
animalia
phylum Proifera
phylum Cnidaria
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum Nematoda
Phylum Annelida
Phylum Mollusca
Phylum Arthropoda
Phylum Echinodermata
Phylum Chordata
protesta
single celled
microscopic
Kingdoms
Factors
biochemistry
how energy is obtained
Cell number
anatomy
fossil records
embryonic development
cell type
protists
animalia
archaea
fungi
plantea
bacterica
Why is it important?
Nature’s Service to Humans and ecosystems
Clean water, clean air, sources of food, soil for agriculture, pollinating effect of many insects, etc.
Medicine
much of our ability to fight diseases and infections (and to find new cures) comes from organisms found all over the world.
Economic Reasons
Lumber, fishery catches, agriculture, livestock, recreation
Species Diversity
The variety of species within an ecosystem.
the health of an ecosystem
to the number and variety of species and ecosystems on earth.
Ecosystem Diversity
the range of physical shapes and sizes of habitats, and the communities in an ecosystem
Genetic Diversity
the variation of genes within the same species
Genetics
monohybrid cross
Homozygous
same alleles
BB
bb
Hetrozygous
different alleles
Bb
protien
chromatin
chromosomes
42 chromosomes
nucleus
cell
karyotype
molecule that is composed of two chains that coil around each other
doulbe helix shape
nucleotides
sugar
phosphate groub
'backbone'
nitrogenous base
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
reproducation
sexual
two parents
half identical
2 processes
fertilization
meiosis
2 stages
cell diviaion
meiosis 2
prophase2
metaphse2
Anaphase 2
Telophase 2
meiosis 1
prophase 1
metaphase 1
Anaphase 1
Telophase 1
off spring through live birth
humans
asexual
one parent
identical
Evolution
Hardy-Weinberg
Gene pool
small colonies
recessive
domianant
The Hardy-Weinberg equations
allele frequency stayed the same
Hardy Weinberg (H-W) conditions
huge population
isolated population (no gene flow)
no natural selection
met the conditio
no mutations
random mating
no evolution happened
allele frequency changed
evolution happeded
Evidence
comparative Anatomy
body structures of species
common ancestory
Anatomical evidence
Analogous Features
Homologous Features
vestigial features
Artificial Selection
choose wanted traits of a species
benificial
adaptable
emprylogy
development of an organism
early stages
Fossils
trace/remains
whole organisms
feces
size and weight
age
teeth
bones
cause of extintion
location/ migration
foot prinet
DNA
biogeography
geographic distribution of species
Habitation patterns
variations in distribution
non migrants
continents theory
Machenism
genetic drift
reducing
The bottleneck effect
wiped out
human actions
natural disaster
the founder effect
colonize
habitat
mutation
DNA sequence
germline
types of germline mutations
point mutations
the nitrogenous base of a DNA sequence
a base gets replace
a base gets removed
a base gets added
chromosome mutations
a whole chromosome
inherated
germ cells (egg and sperm)
Somatic
Evolution
body cells
errors during cell division
Damaged radiation/ chemicals
gene flow
allels
population's migration
genetic variation
natural selection
Directional
extreme traits
Disruptive
over 2 extreme
Sexual
female mate choice
male- male competition
Stablilising
average traits
adapted
reproduction
survival
nonrandom mating