by Sophia Riega 1 year ago
263
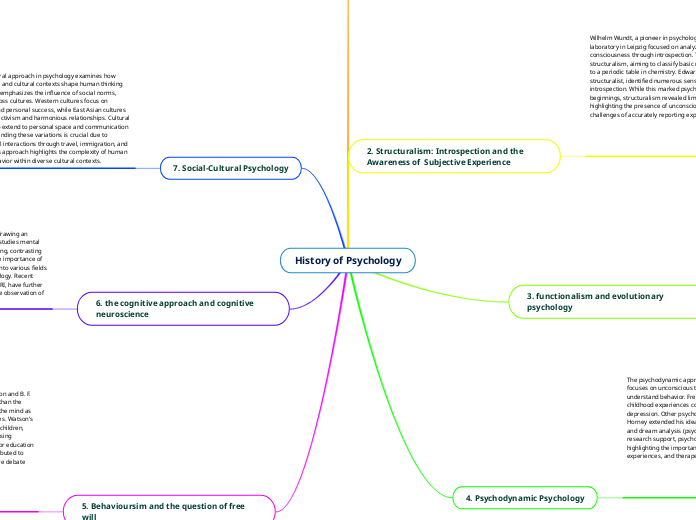
History of Psychology
The evolution of psychology is rooted in the philosophical discussions of ancient Greek thinkers like Plato and Aristotle who pondered nature, nurture, and free will. These debates continued through the Renaissance with figures such as Descartes, but it wasn'