Floating topic
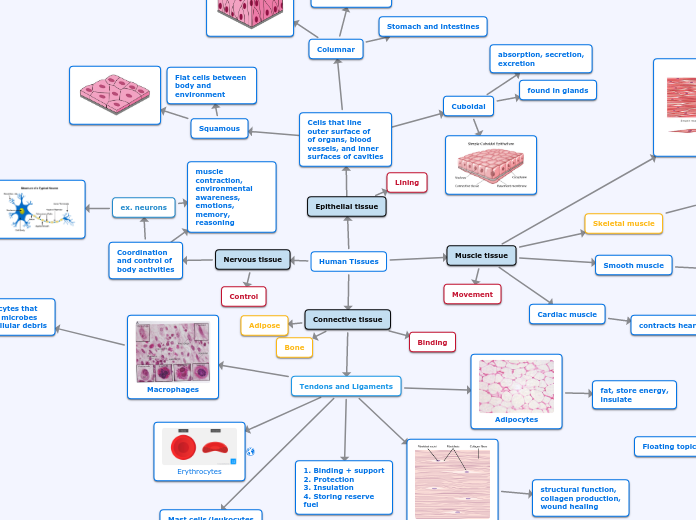
Cuboidal
absorption, secretion,
excretion
found in glands
Cells that line
outer surface of
of organs, blood
vessels, and inner
surfaces of cavities
Columnar
Stomach and intestines
pillar-like cells
that absorb and
excrete
Squamous
Flat cells between
body and
environment
Human Tissues
Connective tissue
Adipose
Bone
Binding
Tendons and Ligaments
Erythrocytes
Mast cells/leukocytes
Immune response
Macrophages
phagocytes that
engulf microbes
and cellular debris
Adipocytes
fat, store energy,
insulate
Fibroblasts
structural function,
collagen production,
wound healing
1. Binding + support
2. Protection
3. Insulation
4. Storing reserve
fuel
Nervous tissue
Control
Coordination
and control of
body activities
ex. neurons
muscle contraction, environmental
awareness, emotions, memory, reasoning
Muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle
moves bones, etc
Movement
Smooth muscle
push food through
intestines and
stomach
Cardiac muscle
contracts heart
Epithelial tissue
Lining