by Jocelyn Cervantes 3 years ago
238
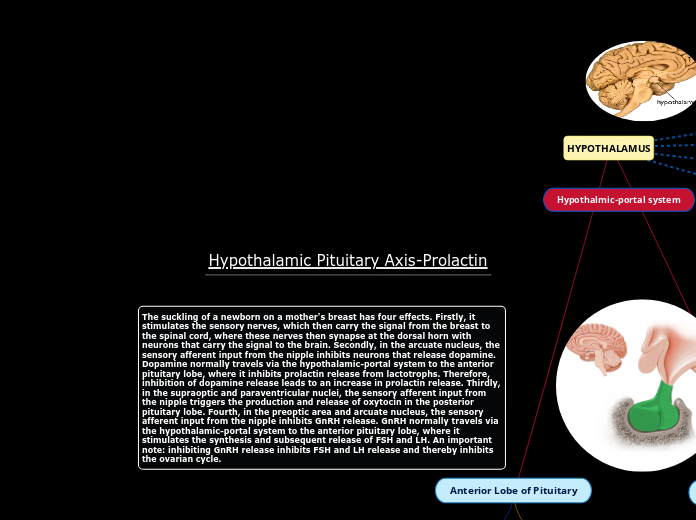
Hypothalamic Pituitary Axis-Prolactin
Prolactin and oxytocin are key hormones produced in the pituitary gland. Prolactin is specifically produced by lactotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland, stored, and then released into the bloodstream.