IMPORT AND EXPORT
Conflict is present everywhere in the world around us. We experience conflict on a daily basis, and it can be minor or major.
Conflict in a story is a struggle between opposing forces. Characters must act to confront those forces and there is where conflict is born. If there is nothing to overcome, there is no story. Conflict in a story creates and drives the plot forward.
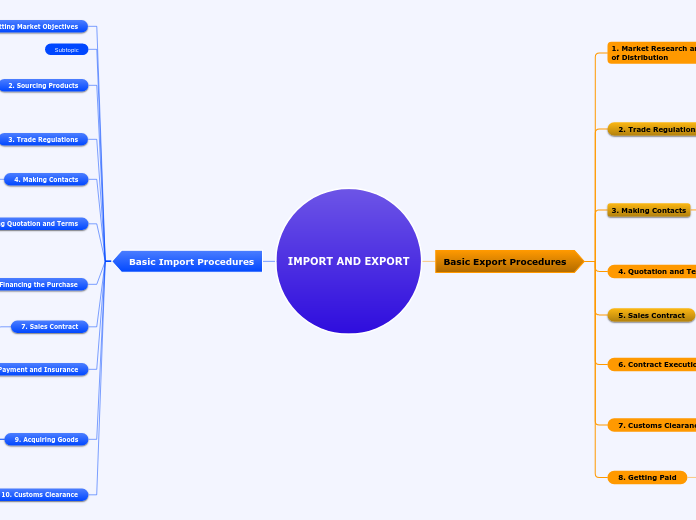
Basic Import Procedures
10. Customs Clearance
• Arranging customs clearance and import declaration
9. Acquiring Goods
• Collecting goods from the specified shipping company or forwarder
• Receiving export documents from the exporter
• Receiving shipping advice and arrival notice
8. Preparing Payment and Insurance
• Subject to the payment terms specified in the sales contract
7. Sales Contract
6. Financing the Purchase
• Types of bank financing and application, such as exporter credit or other bank facilities
• Preparing for working capital
5. Settling Quotation and Terms
• Costs and terms of sale
• Analysing the supplier's quotation and offers
4. Making Contacts
• Sending enquiries to suitable suppliers
3. Trade Regulations
• Patent, trademark and copyright
• Import regulations and requirements, and checking whether import licence is required
2. Sourcing Products
• Sourcing channels of distribution
• Identifying potential suppliers
Subtopic
1. Setting Market Objectives
• Setting market objectives on pricing and terms
Basic Export Procedures
This conflict develops from a protagonist’s inner struggles and may depend on a character trying to decide between good and evil or overcoming self-doubt. This conflict has both internal and external aspects, as obstacles outside the protagonist's force them to deal with inner issues.
8. Getting Paid
7. Customs Clearance
6. Contract Execution
• Subject to the payment terms specified in the sales contract, the exporter should present the required documents to the relevant parties for payment
• Arranging export declaration and applying for export licence when necessary
5. Sales Contract
• Confirming the sales contract and terms of transaction such as payment terms
4. Quotation and Terms
• Costs, quotations and pro forma invoices, and terms of sale
• Making offers and quotation for potential buyers
3. Making Contacts
Give examples of man versus self conflict in the real world.
• Packing and labelling
• Producing or sourcing goods
2. Trade Regulations
• Overseas import regulations and requirements
• Export regulations and requirements
1. Market Research and Setting Objectives of Distribution
Give examples of man versus self conflict in a literary work.
• Selecting target markets, methods of exportation and channels
• Setting foreign market objectives on pricing and terms