by Zalfri Iqwan 4 years ago
354
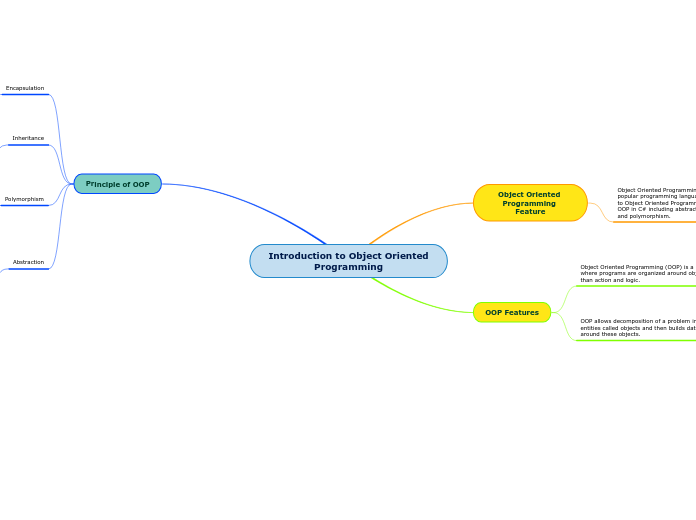
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
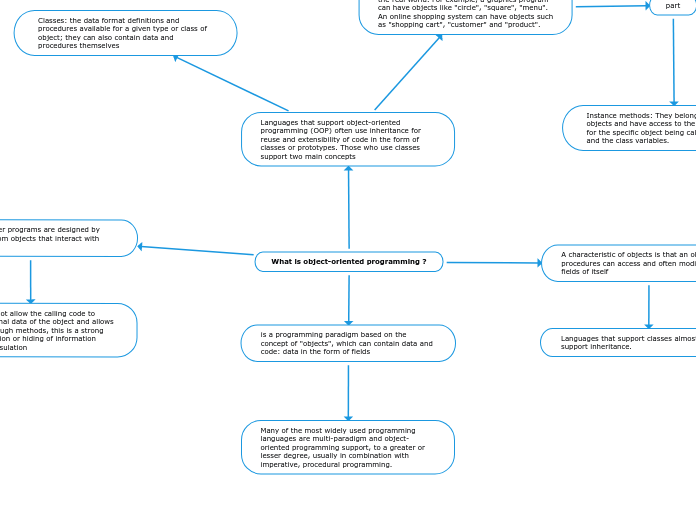
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a paradigm that emphasizes the use of objects to represent both data and behaviors in a program. Key principles of OOP include abstraction, encapsulation, polymorphism, and inheritance.