introductoin to p.s.p
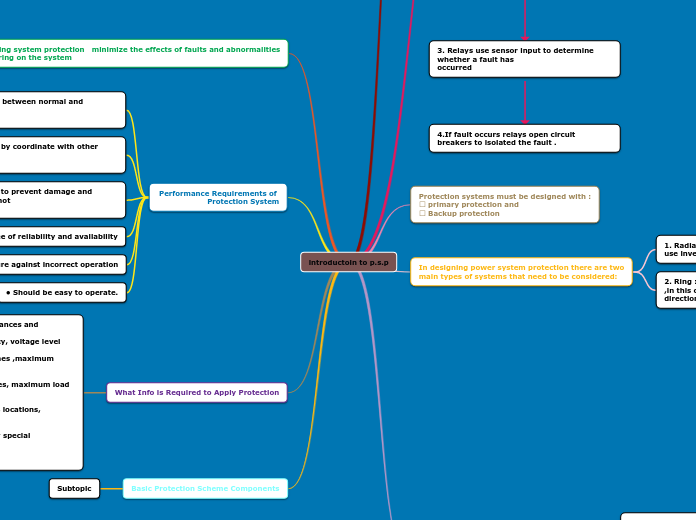
Basic Protection Scheme Components
What Info is Required to Apply Protection
One-line diagram ,Impedances and connections of power
system , system frequency, voltage level and phase
sequence, existing schemes ,maximum allowed clearance
times ,system fault studies, maximum load and system
swing limits ,CTs and VTs locations, connections and ratios,
future expansion and any special considerations for
application
Performance Requirements of Protection System
• Should be easy to operate.
• Secure against incorrect operation
• High degree of reliability and availability
• Fast enough to prevent damage and hazards - but not
too fast.
• Selectivity – by coordinate with other protection
systems.
• Discriminate between normal and abnormal
conditions.
• No unprotected zones "blind spots
Planning system protection minimize the effects of faults and abnormalities
occurring on the system
a) Quickly isolate faulted zone
b) Minimize the magnitude of short-circuit current and,
minimize potential damage to the system.
c) Provide alternate circuits, automatic transfers, or automatic
reclosing devices, in order to minimize the duration
outages.
Protection against faults and abnormalities
b) Abnormalities
Under and over frequency
Power swings.
Overload and over temperature
Overvoltage or under voltage.
Under excitation of synchronous machines
Over fluxing of power transformers
Asynchronous operation of synchronous machines
Mechanical defects i.e. leaking oil, tap changer
mechanism faults etc
a) Faults : The principal electrical system faults are:
short circuits and overloads.
Subtopic
Short circuits: failure of insulation , mechanical
damage to electrical distribution equipment, failure of
equipment as a result of overloading or other. be solid or has relatively low
impedance
Effects of Short-Circuit Type Faults
4) Electric current leakage flow that could create a
hazard to people
3) large mechanical forces which have potential to
break or damage equipment.
2) Arcs, sparking and the heating effect can start fires
1) Large current can be involved. This cause
equipment and generators would be damaged. Only be allowed to flow for a very short time as 10ms
up to say 3 seconds .
Causes of Short-Circuit Faults:
• Insulation breakdown, Birds and animals ,diggers for
underground cables, poles collapsing, conductors
breaking, vehicle impact ,wind effect ,incorrect
operation by personnel..and so
Typical Short-Circuit Type Distribution
Single-Phase-Ground: 70 - 80 %
Phase-Phase-Ground: 17 - 10 %
Phase-Phase: 10 - 8 %
Three-Phase: 3 - 2 %
In designing power system protection there are two
main types of systems that need to be considered:
2. Ring : power can flow in both direction ,in this case
directional overcurrent relay is used.
1. Radial: The protection systems usually use inversetime overcurrent relays
Protection systems must be designed with :
primary protection and
Backup protection
Fault sequence of events
1. Fault occurs somewhere on the system, changing the system
currents and voltages parameters.
2. Current transformers (CTs) and potential transformers (PTs)
sensors detect the change in currents/voltages
3. Relays use sensor input to determine whether a fault has
occurred
4.If fault occurs relays open circuit breakers to isolated the fault .
The objectives of power system protection are to:
Minimize damage to the system components
Limit the extent and duration of service interruption
thought the protection zone