by Carol Steffes 5 years ago
194
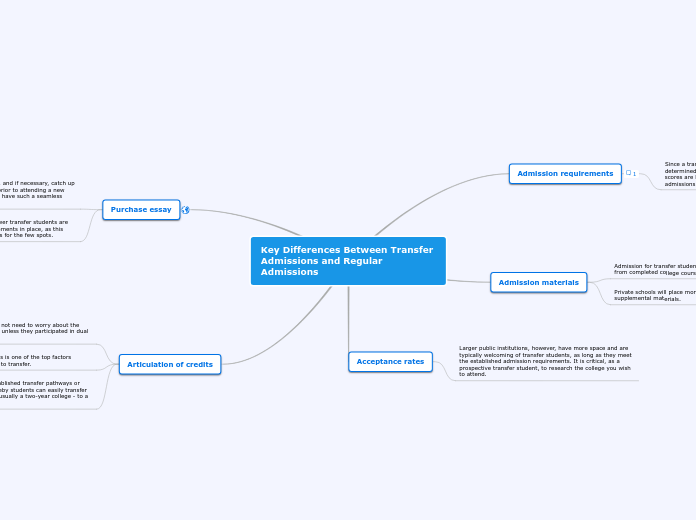
Key Differences Between Transfer Admissions and Regular Admissions
Transfer admissions and regular admissions differ significantly in various aspects including credit articulation, admission materials, acceptance rates, and requirements. For transfer students, credit articulation is a critical factor, especially when moving from a two-year to a four-year institution.