by Marco Mazzantini 4 years ago
752
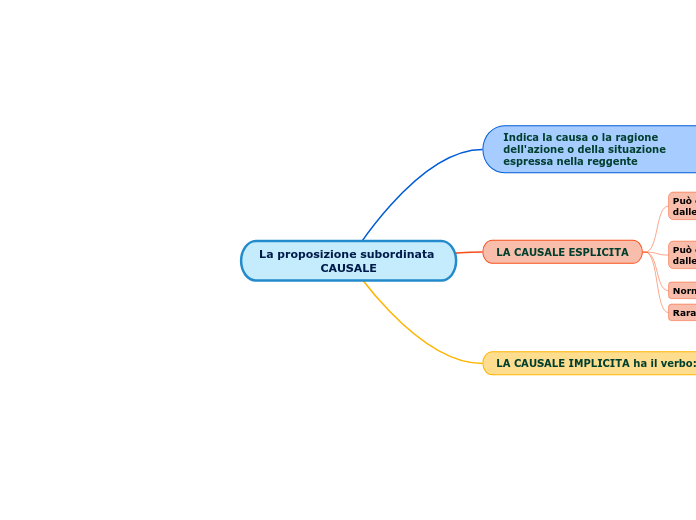
La proposizione subordinata CAUSALE
by Marco Mazzantini 4 years ago
752

More like this
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms.
This energy is released when the nuclei are combined (fusion) or split apart (fission).
Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms to produce electricity.
What element do they use to fuel nuclear power plants?
Thermal energy is created from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances. The faster they move, the more energy they possess and the hotter they become. Thermal energy is also called heat energy.
Give examples of heat energy.
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.