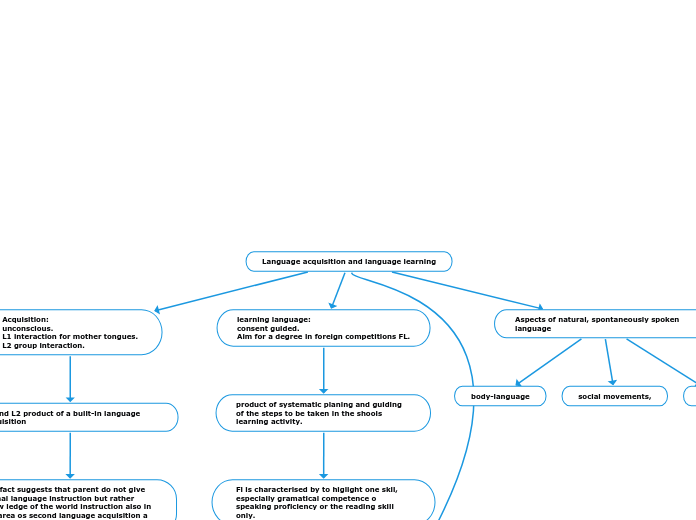
Language acquisition and language learning
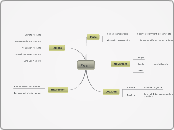
Typos of signs and meanings
sings meanings
verbal signs
1. connotatively laden words, 2. dialect and role varieties 3.grammatical system
non-verbal signs
vocal signs
tone of vouice, ie pitch, loudness, etc, modulation.
body signs
body language, social, movements, kinesics.
1.expresive. 2. social. 3. referential
Aspects of natural, spontaneously spoken language
kinesics,
social movements,
body-language
learning language:
consent guided.
Aim for a degree in foreign competitions FL.
product of systematic planing and guiding of the steps to be taken in the shools learning activity.
Fl is characterised by to higlight one skil, especially gramatical competence o speaking proficiency or the reading skill only.
Acquisition:
unconscious.
L1 interaction for mother tongues.
L2 group interaction.
L1 and L2 product of a built-in language adquisition
this fact suggests that parent do not give formal language instruction but rather know ledge of the world instruction also in the area os second language acquisition a lot of conscloos and deliberate take places.
wode (1976) y felix (1977) call "naturalistic"language acquisition is unconscious and non guided.