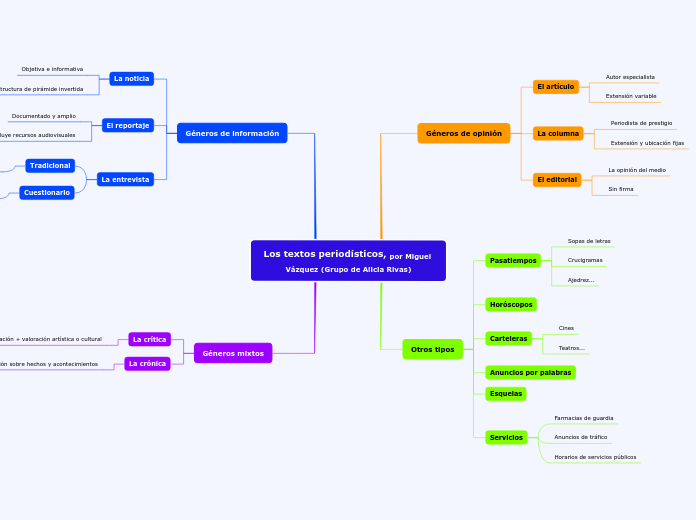
Los textos periodísticos, por Miguel Vázquez (Grupo de Alicia Rivas)
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Géneros mixtos
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
La crónica
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
Exposición y reflexión sobre hechos y acontecimientos
La crítica
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
Información + valoración artística o cultural
Géneros de información
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
La entrevista
Cuestionario
Siempre las mismas preguntas
Tradicional
Es personal y admite improvisación
El reportaje
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Incluye recursos audiovisuales
Documentado y amplio
La noticia
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Estructura de pirámide invertida
Objetiva e informativa
Otros tipos
Servicios
Horarios de servicios públicos
Anuncios de tráfico
Farmacias de guardia
Esquelas
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
Anuncios por palabras
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the car with his mother.
Carteleras
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
Teatros...
Cines
Horóscopos
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
Pasatiempos
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Ajedrez...
Crucigramas
Sopas de letras
Géneros de opinión
El editorial
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Sin firma
La opinión del medio
La columna
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
Extensión y ubicación fijas
Periodista de prestigio
El artículo
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
Extensión variable
Autor especialista