by Philip Breen 6 years ago
295
Macromolocules
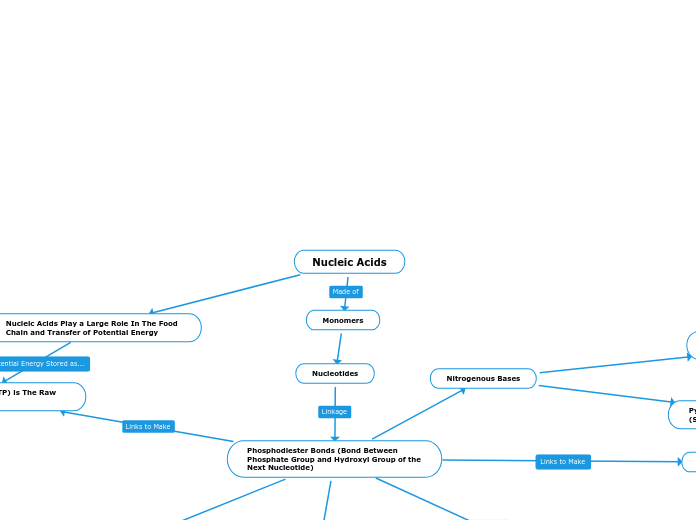
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules essential for life, encompassing lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. Lipids, including fats, oils, and steroids, are primarily hydrophobic and serve functions such as energy storage, insulation, and cushioning of organs.