by Enric Folch Prim 1 year ago
168
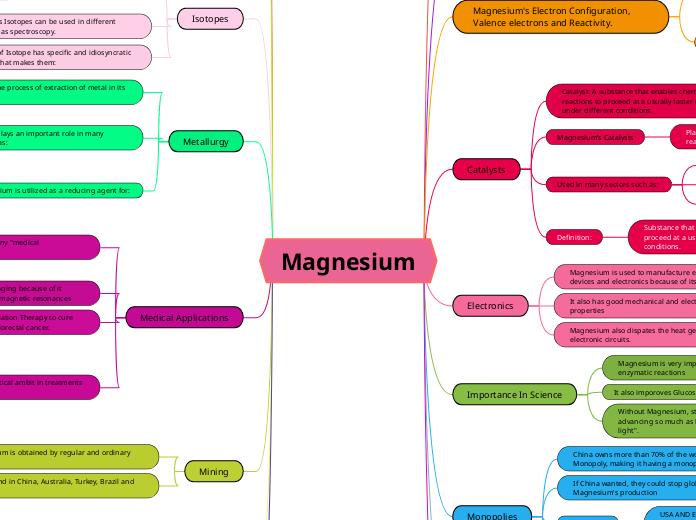
Magnesium
Magnesium is a versatile element with significant importance in various industrial sectors including aviation, aerospace, and automobile industries. It is utilized as a reducing agent and an additive in alloys due to its reactivity and strong, lightweight properties.