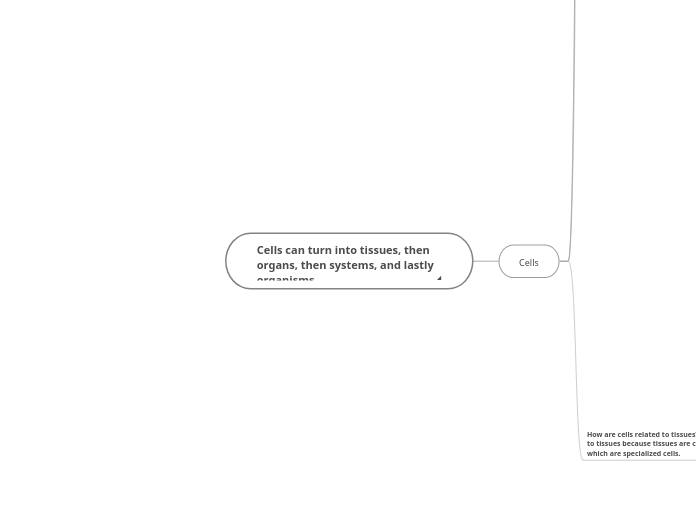
Cells can turn into tissues, then organs, then systems, and lastly organisms
Cells
How are cells related to tissues? Cells are related to tissues because tissues are clusters of cells, which are specialized cells.
Tissues
How are tissues related to organs? Tissues are related to organs because tissues group together and form an organ.
Organs
How are organs related to systems? A group of organs forms into different types of systems such as respiratory system, digestive system and more.
Organisms
How is the whole system including cells, tissues and organs related to organisms? That's because the whole system relies on organisms because humans are organisms so without organisms there isn't any animals on earth which means there is no need for the whole system.
Subtopic
The types of organisms are
Producers- Generates its own nourishment from basic resources
Consumers- relies on plants or other animals for nourishment
Herbivores- Exclusively eats grass, herbs, leaves, fruits, and other plant components
Carnivores- consumes the flesh of other animals Omnivores- Consumes both plants and animals Scavengers- Consumes dead and rotting biomass Parasites- relies upon there recipient for survival Predators- hunts and kills their prey in order to survive
Decomposers-
An organism is any living system that operates as a separate entity. All organisms are made up of cells.
How are organisms related to cells, tissues, organs and systems?
Systems
Body systems are collections of organs that cooperate to carry out particular tasks for the body. These processes interact with several bodily systems. The digestive, circulatory, nervous, respiratory, skeletal, and muscular systems are a few of the major body systems.
A group of organs that cooperate to carry out one or more functions is known as an organ. Each organ in a plant or animal body is composed of certain tissues and serves a specific purpose.
Animal tissue examples and definitions:
Connective tissue: they affix tissues and organs together, I In the form of adipose tissues, they store fat, They aid in tissue healing, they guard against mechanical shocks to the organs, the organs assist in defense as well.
Epithelial tissue- The inner lining and protective coating of the body and organs are made up of epithelial tissues.
Muscle tissue- consisting of cells with the unique capacity to contract or shorten and result in the movement of various bodily components.
Nervous tissue- It is in charge of coordinating and controlling many bodily activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, raises awareness of the environment, and plays an important role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.
Animal tissues are defined as collections of cells that work together to fulfil specific functions. Animals have four different tissue kinds, and each type has a unique structure and purpose. They are: epithelial tissues, connective tissues, muscular tissues, nerve tissues, and lastly, connective tissues.
Examples and definitions of the cell parts:
Cell membrane- It protects the cells from external injury.
Cell wall- The passage of substances into and out of cells is regulated by the cell membrane.
Cell organelles
Nucleolus- The nucleus is also referred to as the "brain" or "control center" of the cell.
nuclear membrane
endoplasmic reticulum- the procedure for creating new proteins, changing them, and directing them
Golgi bodies- is in charge of moving, altering, and packing lipids and proteins into vesicles for distribution to specific locations.
ribosome is in charge of moving, altering, and packing lipids and proteins into vesicles for distribution to specific locations.
mitochondria- is to control cellular metabolism and produce the energy currency of the cell through respiration. They are therefore also referred to as "the powerhouse of the cell."
lysosomes- engaged in the removal of trash and digestion
chloroplast- convert sunlight into food by using photosynthesis.
vacuoles- Food or any other type of nutrient that a cell may require to survive may be stored in vacuoles.
The cell is a necessity, structural, and functional unit of all living things is called a cell. You need cells for all living things. There are 200 types of cells including red blood cells, skin cells etc. Cells relate to tissues because a group of cells are tissues.