Modernism (1900-1950)
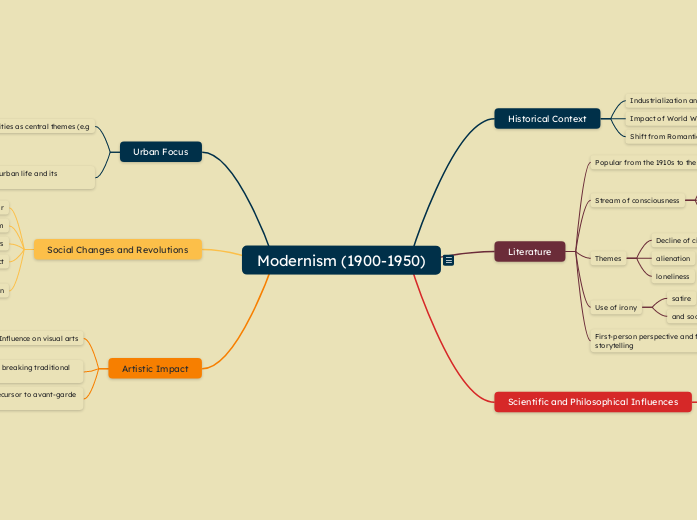
Modernism (1900-1950): Mind Map
1. Historical Context
Industrialization and globalization.
Impact of World War I and World War II.
Shift from Romanticism to Modernism.
2. Literature
Popular from the 1910s to the 1960s.
Stream of consciousness: focus on inner emotions (e.g., James Joyce, Virginia Woolf).
Themes: Decline of civilization, alienation, loneliness.
Use of irony, satire, and social criticism.
First-person perspective and fragmented storytelling.
3. Scientific and Philosophical Influences
Explosion of scientific innovation (Einstein, technological advances like motorcars and telephones).
Influence of Darwin's Theory of Evolution (pessimism about human destiny).
Sigmund Freud's theories on the unconscious and inner life.
4. Urban Focus
Cities as central themes (e.g., Paris, London, Chicago, New York).
Writers' fascination with urban life and its anonymity.
5. Social Changes and Revolutions
Fall of the British Empire (Boer War, post-WWI).
Rise of communism.
Women's suffrage movement and its effects.
Education Act: mandatory schooling for children.
Urbanization: 70% of populations in cities, growth of anonymity.
6. Artistic Impact
Influence on visual arts, music, and architecture.
Emphasis on innovation and breaking traditional rules.
Modernism's legacy as a precursor to avant-garde movements.
Artistic Impact
Modernism's legacy as a precursor to avant-garde movements
Emphasis on innovation and breaking traditional rules
Influence on visual arts
and architecture
music
Social Changes and Revolutions
Urbanization
growth of anonymity
70% of populations in cities
Education Act
mandatory schooling for children
Women's suffrage movement and its effects
Rise of communism
Fall of the British Empire (Boer War
post-WWI)
Urban Focus
Writers' fascination with urban life and its anonymity
Cities as central themes (e.g
New York)
Chicago
London
Paris
Scientific and Philosophical Influences
Sigmund Freud's theories on the unconscious and inner life
Influence of Darwin's Theory of Evolution (pessimism about human destiny)
Explosion of scientific innovation (Einstein
technological advances like motorcars and telephones)
Literature
First-person perspective and fragmented storytelling
Use of irony
and social criticism
satire
Themes
loneliness
alienation
Decline of civilization
Stream of consciousness
Virginia Woolf)
James Joyce
focus on inner emotions (e.g
Popular from the 1910s to the 1960s
Historical Context
Shift from Romanticism to Modernism
Impact of World War I and World War II
Industrialization and globalization